Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Radiol. Nov 28, 2014; 6(11): 850-854
Published online Nov 28, 2014. doi: 10.4329/wjr.v6.i11.850
Published online Nov 28, 2014. doi: 10.4329/wjr.v6.i11.850
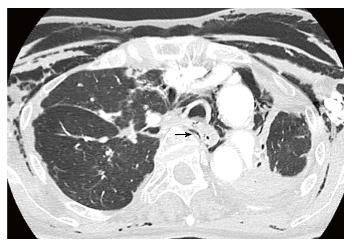
Figure 1 Chest computed tomography scan of an 82-year-old woman shows an injury to the posterior wall of the trachea, massive pneumomediastinum, and subcutaneous emphysema due to ruptured pars membranosa (arrow).
- Citation: Murayama S, Gibo S. Spontaneous pneumomediastinum and Macklin effect: Overview and appearance on computed tomography. World J Radiol 2014; 6(11): 850-854
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1949-8470/full/v6/i11/850.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4329/wjr.v6.i11.850