Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Radiol. Oct 28, 2014; 6(10): 840-845
Published online Oct 28, 2014. doi: 10.4329/wjr.v6.i10.840
Published online Oct 28, 2014. doi: 10.4329/wjr.v6.i10.840
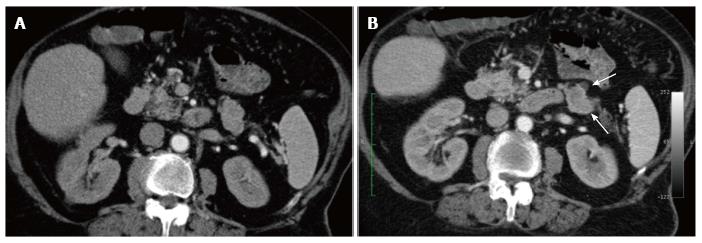
Figure 1 Contrast-enhanced multi-detector computed tomography: Transverse 3 mm thick images of arterial (A) and pancreatic phase (B) are shown.
Computed tomography findings were prospectively considered negative as no definite hyper-vascular lesion could be appreciated. Retrospectively, a mildly, inhomogeneously enhancing lesion could be appreciated at the level of the pancreatic tail (arrow-head) with a small cyst on its anterior margin (arrow), both more conspicuous on the pancreatic phase (B) than in the arterial phase (A) measuring 79 vs 67 HU, respectively. In both images a faint cortico-medullary nephrogram is depicted due to the chronic renal insufficiency.
- Citation: Camera L, Severino R, Faggiano A, Masone S, Mansueto G, Maurea S, Fonti R, Salvatore M. Contrast enhanced multi-detector CT and MR findings of a well-differentiated pancreatic vipoma. World J Radiol 2014; 6(10): 840-845
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1949-8470/full/v6/i10/840.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4329/wjr.v6.i10.840