Copyright
©2013 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Radiol. Aug 28, 2013; 5(8): 275-284
Published online Aug 28, 2013. doi: 10.4329/wjr.v5.i8.275
Published online Aug 28, 2013. doi: 10.4329/wjr.v5.i8.275
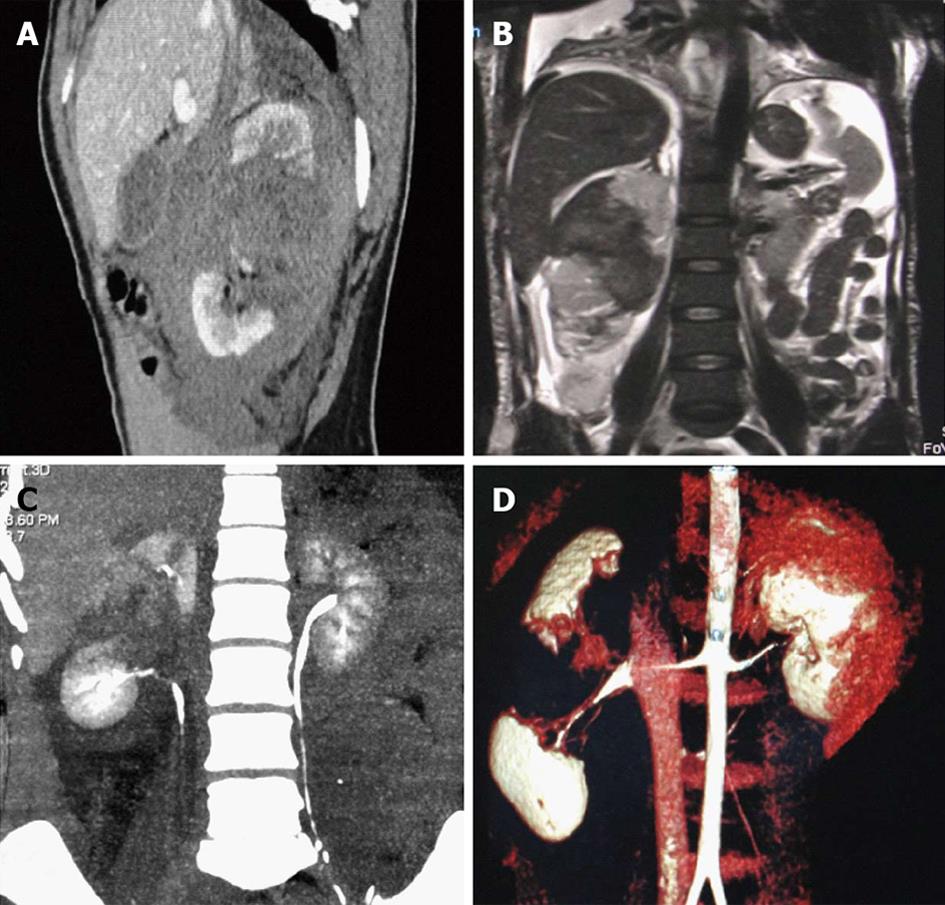
Figure 7 Grade IV injury.
Fractured kidney. Contrast enhanced computed tomography (CECT) and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) images of a 58-year-old female patient who sustained renal tubular acidosis and had significant hematuria. A: Sagittal CECT; B: Coronal T2 weighted MRI section showing a large laceration with hematoma extending through the mid pole of the right kidney dividing the kidney into two parts and separating the poles wide apart; C: Coronal maximum intensity projection image of the excretory phase did not show any urinary leak with opacification of the ureter; D: Volume rendered reconstructed image showing the fractured kidney through its waist.
- Citation: Dayal M, Gamanagatti S, Kumar A. Imaging in renal trauma. World J Radiol 2013; 5(8): 275-284
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1949-8470/full/v5/i8/275.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4329/wjr.v5.i8.275