Copyright
©2013 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Radiol. Aug 28, 2013; 5(8): 275-284
Published online Aug 28, 2013. doi: 10.4329/wjr.v5.i8.275
Published online Aug 28, 2013. doi: 10.4329/wjr.v5.i8.275
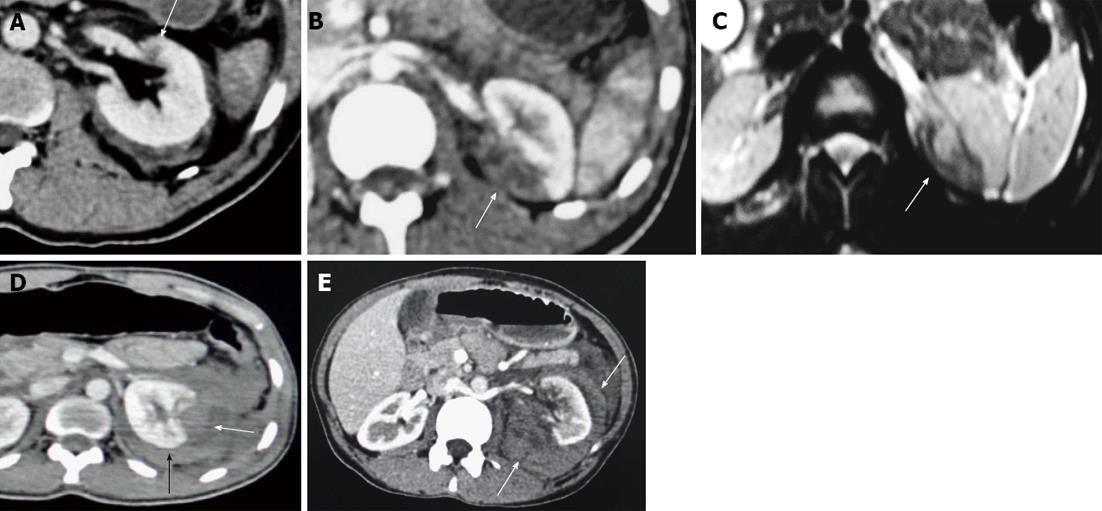
Figure 1 Terminology constellation.
A: Contusion. Axial contrast enhanced computed tomography (CECT) section showing an ill-defined and poorly marginated hypodense area of decreased enhancement (arrow) suggestive of intra-parenchyma contusion; B, C: Infarction; B: Axial CECT; C: Axial T2 weighted magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) image showing infarcts as wedge shaped, sharply marginated hypodense area on computed tomography (arrow) and hypointense area on T2W MRI image (arrow); D: Subcapsular hematoma. Axial CECT section showing hypodense area of blood collection along the renal contour causing flattening or depression of the underlying renal surface (arrow). Also, there is associated perirenal hematoma (black arrow); E: Perirenal hematoma. Axial CECT image showing hypodense area of fluid collection (arrows) around the left kidney confined within the Gerota’s fascia and not producing flattening of the renal contour.
- Citation: Dayal M, Gamanagatti S, Kumar A. Imaging in renal trauma. World J Radiol 2013; 5(8): 275-284
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1949-8470/full/v5/i8/275.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4329/wjr.v5.i8.275