Copyright
©2013 Baishideng.
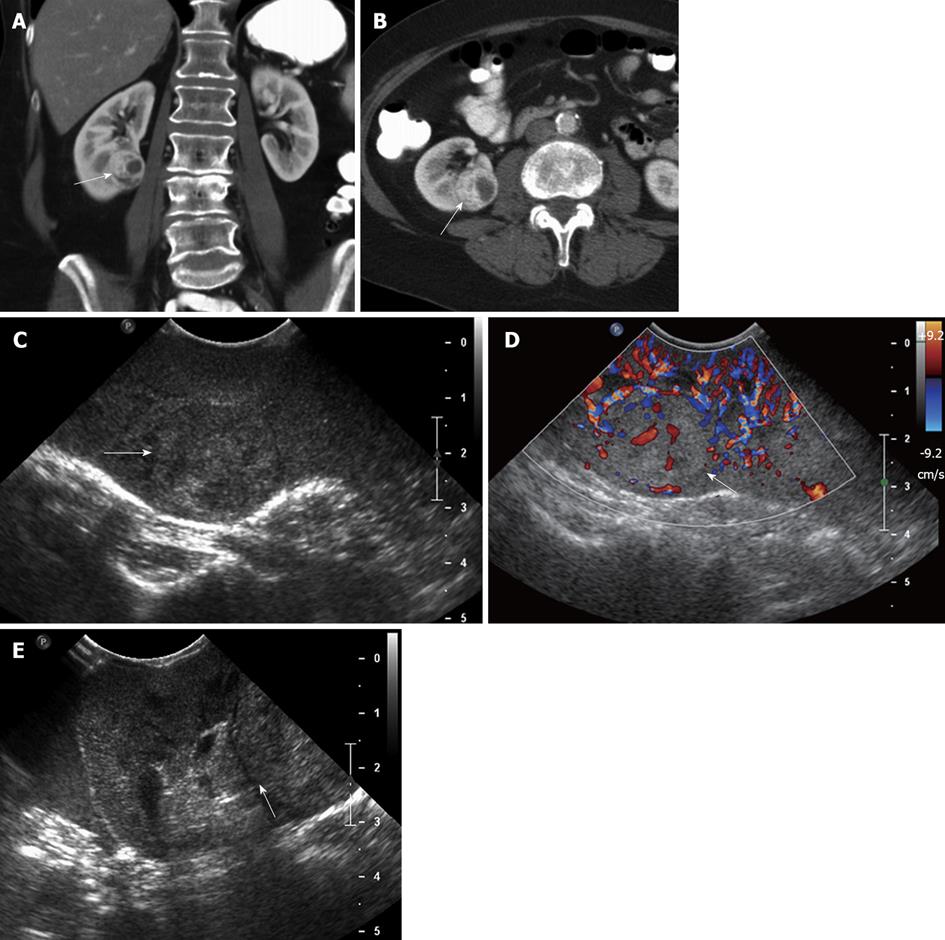
Figure 5 A 62-year-old female with renal cell carcinoma.
A, B: Coronal (A) and axial (B) contrast-enhanced computed tomography images show a solid, hypervascular, 2.8 cm mass in the midportion - lower pole of the right kidney, consistent with a renal cell carcinoma; C, D: Intraoperative grayscale (C) and color Doppler ultrasound (D) identify a solid echogenic mass in the midportion - lower pole of the right kidney, with evidence of internal vascularity, consistent with a renal cell carcinoma; E: Intraoperative ultrasound image in a oblique transverse plane shows that the lesion abuts the hyperechoic renal sinus fat. This important information to guide the surgeon, in order that tumor-free margins are properly obtained at the time of resection.
- Citation: Marcal LP, Patnana M, Bhosale P, Bedi DG. Intraoperative abdominal ultrasound in oncologic imaging. World J Radiol 2013; 5(3): 51-60
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1949-8470/full/v5/i3/51.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4329/wjr.v5.i3.51