Copyright
©2013 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Radiol. Dec 28, 2013; 5(12): 491-497
Published online Dec 28, 2013. doi: 10.4329/wjr.v5.i12.491
Published online Dec 28, 2013. doi: 10.4329/wjr.v5.i12.491
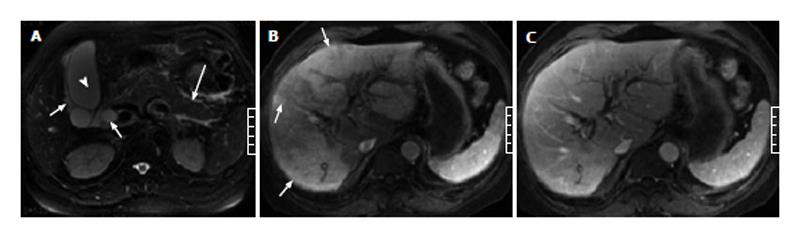
Figure 1 A 65-year-old man with acute pancreatitis combined with cholecystitis as well as common bile duct and intrahepatic bile duct dilatation.
Fast recovery fast spin-echo T2-weighted image (A) shows gallbladder distention (arrowhead), perigallbladder fluid (short arrow), common bile duct dilatation (short arrow), and peripancreatic strand hyperintensity signal (long arrow). Patch- or wedge-shaped hepatic abnormal perfusion is found in the left and right lobes of the liver on the artery phase images (B, arrow) and returns to normal on the venous phase images (C).
- Citation: Tang W, Zhang XM, Zhai ZH, Zeng NL. Hepatic abnormal perfusion visible by magnetic resonance imaging in acute pancreatitis. World J Radiol 2013; 5(12): 491-497
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1949-8470/full/v5/i12/491.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4329/wjr.v5.i12.491