Copyright
©2013 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Radiol. Dec 28, 2013; 5(12): 460-467
Published online Dec 28, 2013. doi: 10.4329/wjr.v5.i12.460
Published online Dec 28, 2013. doi: 10.4329/wjr.v5.i12.460
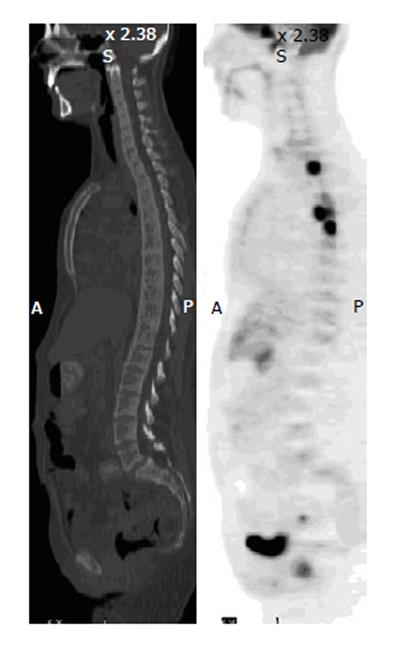
Figure 13 Lymphomatous disease of bone.
A 28-year-old man with disseminated B-cell lymphoma had fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography-computer tomography (PET-CT) for initial staging. Sagittal PET image shows foci of intense uptake in the vertebral bodies of the upper thoracic spine, but the CT is unremarkable in the corresponding sites. Repeated scan 3 mo after chemotherapy demonstrate resolution of uptake in the bones as well as lungs and lymph nodes.
- Citation: Liu Y. Fluorodeoxyglucose uptake in absence of CT abnormality on PET-CT: What is it? World J Radiol 2013; 5(12): 460-467
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1949-8470/full/v5/i12/460.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4329/wjr.v5.i12.460