Copyright
©2013 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Radiol. Oct 28, 2013; 5(10): 381-385
Published online Oct 28, 2013. doi: 10.4329/wjr.v5.i10.381
Published online Oct 28, 2013. doi: 10.4329/wjr.v5.i10.381
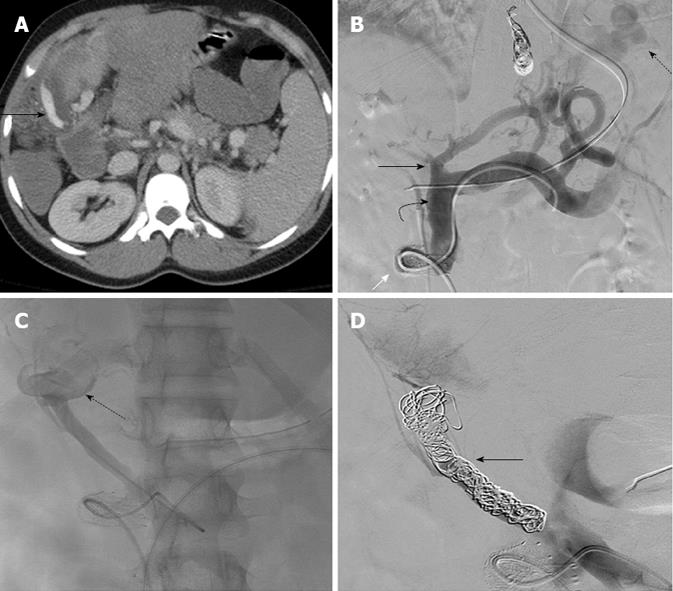
Figure 2 Case 2: Traumatic hemorrhage from a jejunal varix.
A: Contrast enhanced computed tomography axial image shows contrast extravasation tracking along the outer wall of the hepatico-jejunostomy loop (arrow); B: Venogram performed by a trans meso-caval shunt (white arrow) approach shows large gastric fundal varices (dotted arrow), dilated superior mesenteric vein (curved arrow). The main portal vein is obliterated (black arrow); C: Selective venogram of the hepaticojejunostomy loop branch of the superior mesenteric vein shows dilatation of this branch with active extravasation of the contrast from the hepaticojejunostomy loop (dotted arrow); D: Multiple coils were used to occlude the branch (arrow).
- Citation: Sundarakumar DK, Smith CM, Lopera JE, Kogut M, Suri R. Endovascular interventions for traumatic portal venous hemorrhage complicated by portal hypertension. World J Radiol 2013; 5(10): 381-385
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1949-8470/full/v5/i10/381.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4329/wjr.v5.i10.381