Copyright
©2012 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Radiol. Jul 28, 2012; 4(7): 302-310
Published online Jul 28, 2012. doi: 10.4329/wjr.v4.i7.302
Published online Jul 28, 2012. doi: 10.4329/wjr.v4.i7.302
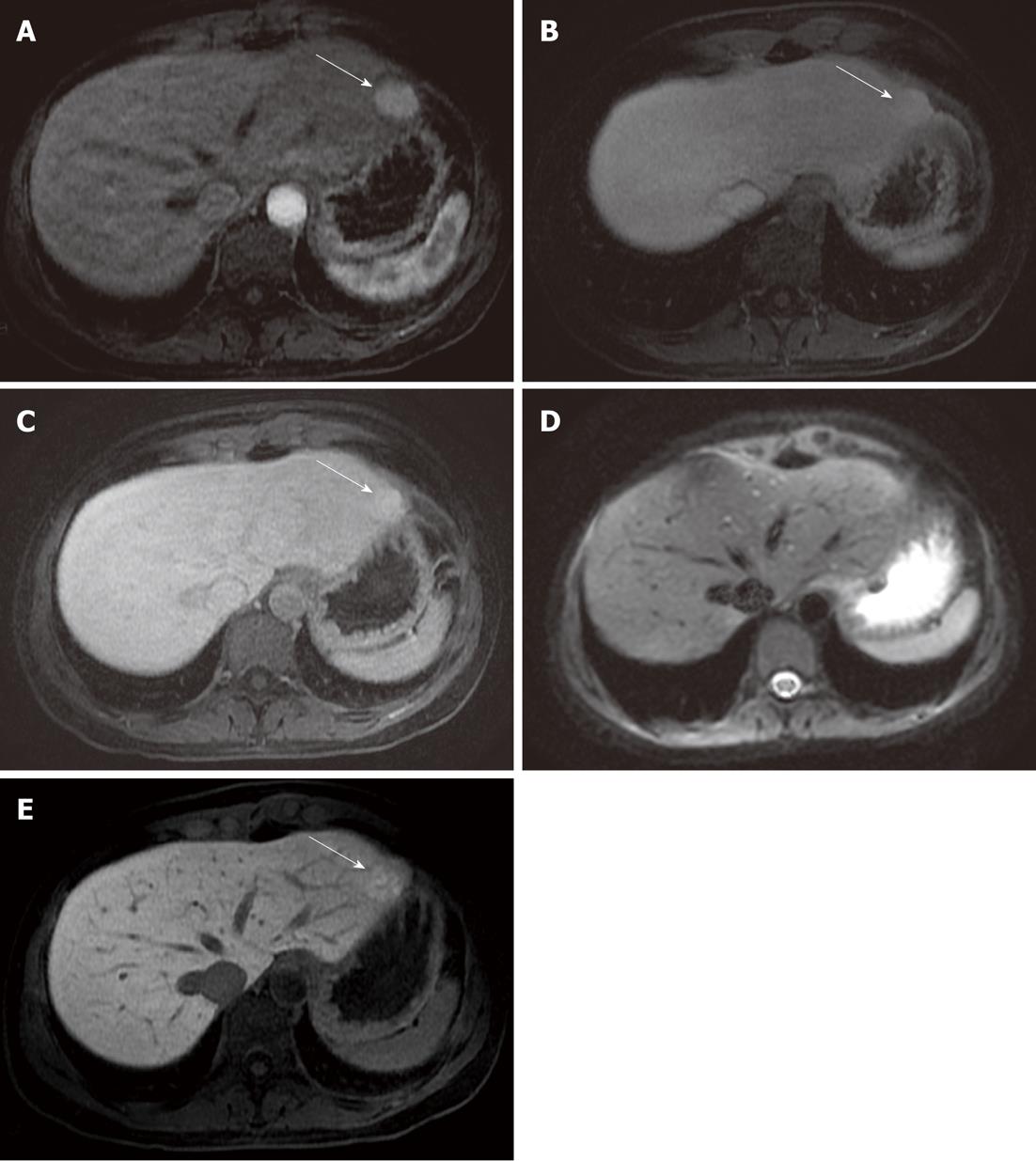
Figure 2 Focal nodular hyperplasia found in the left liver lobe (arrow).
A: A round-shaped solid lesion (arrow) is depicted in the left liver lobe (in the II segment); B, C: The lesion (arrow) appears homogeneously hyperintense in the arterial phase, and remains slightly hyperintense in the portal and in the equilibrium phase; D: The lesion was missed on the diffusion image by both readers, probably due to its location near the gastric wall, along the liver surface; E: In the hepato-specific phase, the lesion (arrow) shows uptake of gadolinium-ethoxybenzyl-diethylenetriamine pentaacetic acid; a diagnosis of focal nodular hyperplasia was suggested due to the dynamic behavior observed after contrast administration.
- Citation: Palmucci S, Mauro LA, Messina M, Russo B, Failla G, Milone P, Berretta M, Ettorre GC. Diffusion-weighted MRI in a liver protocol: Its role in focal lesion detection. World J Radiol 2012; 4(7): 302-310
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1949-8470/full/v4/i7/302.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4329/wjr.v4.i7.302