Copyright
©2012 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Radiol. May 28, 2012; 4(5): 231-235
Published online May 28, 2012. doi: 10.4329/wjr.v4.i5.231
Published online May 28, 2012. doi: 10.4329/wjr.v4.i5.231
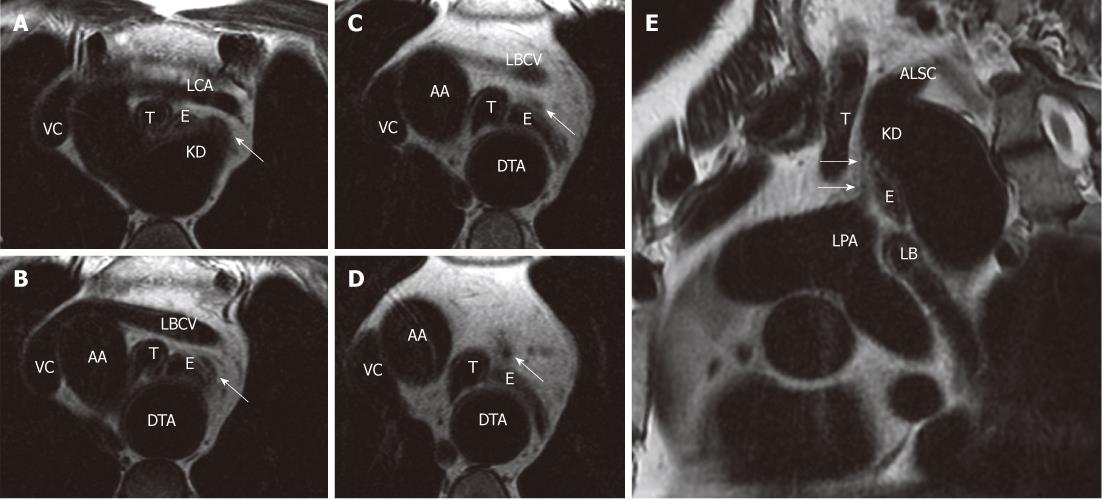
Figure 3 Four sequential frFSE T2-weighted cardiac-gated axial images (A-D) and sequence (E).
A-D: The ligamentum arteriosum from its proximal attachment on Kommerell’s diverticulum (KD) to its distal anchorage site on the superior aspect of the left pulmonary artery (LPA) origin; E: The complete course of the ligamentum arteriosum, which is appreciable anteriorly to the esophagus and trachea. Arrows indicate ligamentum arteriosum. VC: Vena cava; LBCV: Left brachio-cephalic vein; T: Trachea; E: Esophagus; LCA: Left common carotid artery; AA: Ascending aorta; DTA: Descending thoracic aorta; ALSC: Aberrant left subclavian artery.
- Citation: Paparo F, Bacigalupo L, Melani E, Rollandi GA, De Caro G. Cardiac-MRI demonstration of the ligamentum arteriosum in a case of right aortic arch with aberrant left subclavian artery. World J Radiol 2012; 4(5): 231-235
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1949-8470/full/v4/i5/231.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4329/wjr.v4.i5.231