Copyright
©2012 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
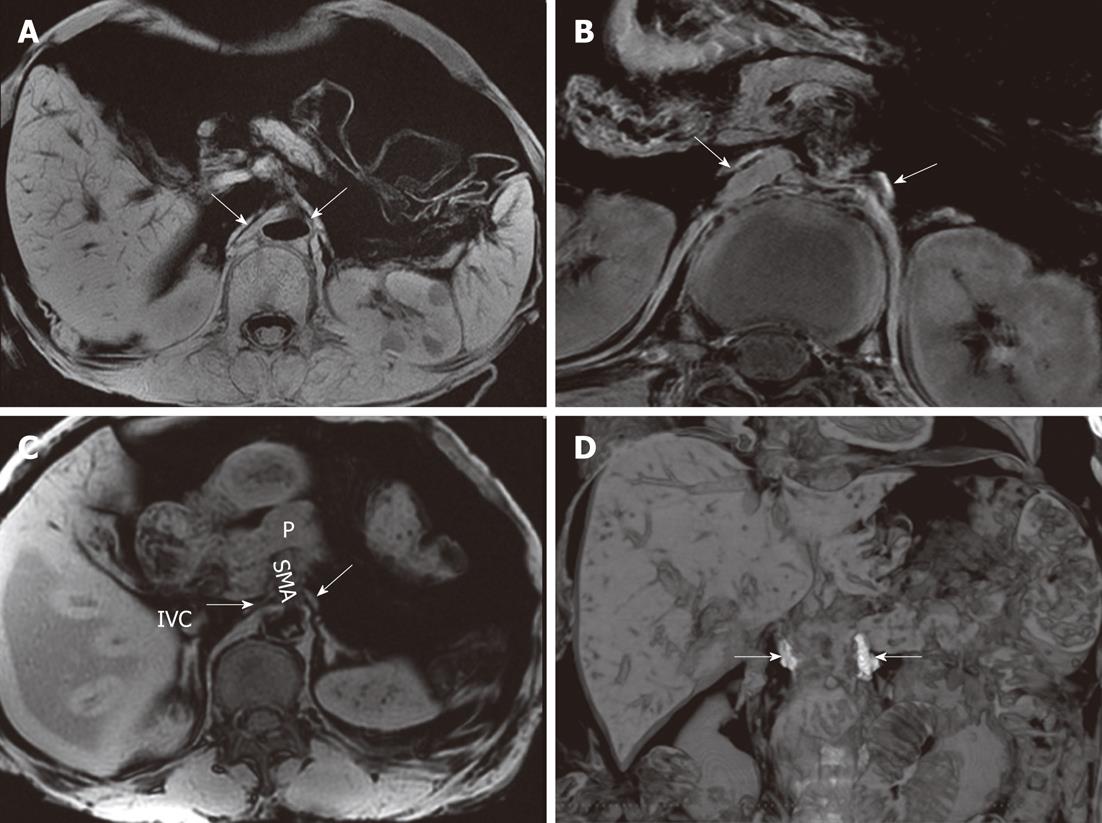
Figure 13 The celiac ganglia on an magnetic resonance imaging.
A: A gradient-refocused-echo T1-weighted image shows that both the right and left celiac ganglia (arrows), labeled with Gd-DTPA, have a higher signal intensity than that of the viscus, such as the liver and spleen; B: 3D T1-weighted image shows that both the right and left celiac ganglia labeled with Gd-DTPA (arrows) have a higher signal intensity than the kidneys; C: A gradient-refocused-echo, T1-weighted, out-of-phase image shows the right and left celiac ganglia (labeled with arrows). The right celiac ganglion was located in the space formed by the inferior vena cava (IVC), right adrenal gland, right diaphragmatic crura, head of pancreas, and superior mesenteric artery (SMA). The left ganglion was located in the open space formed by the left adrenal gland, left diaphragmatic crura, and SMA. The celiac ganglia are labeled with gadolinium; D: Coronal imaging on T1-weighted images shows the celiac ganglia labeled with Gd-DTPA (arrows). P: Pancreas.
- Citation: Zuo HD, Zhang XM, Li CJ, Cai CP, Zhao QH, Xie XG, Xiao B, Tang W. CT and MR imaging patterns for pancreatic carcinoma invading the extrapancreatic neural plexus (Part I): Anatomy, imaging of the extrapancreatic nerve. World J Radiol 2012; 4(2): 36-43
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1949-8470/full/v4/i2/36.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4329/wjr.v4.i2.36