Copyright
©2012 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Radiol. Oct 28, 2012; 4(10): 439-442
Published online Oct 28, 2012. doi: 10.4329/wjr.v4.i10.439
Published online Oct 28, 2012. doi: 10.4329/wjr.v4.i10.439
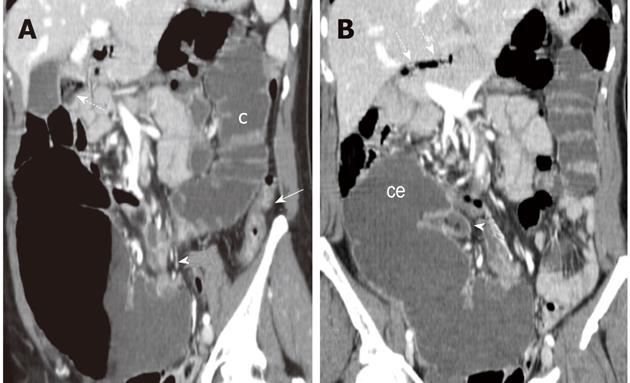
Figure 3 Multi-detector contrast-enhanced computed tomography.
Reformatted images on an oblique coronal (A) and on the coronal plane (B) are shown. In A, colonic segments (c) distal to the transition zone (arrowhead) also appeared distended by fluid throughout the splenic flexure with a collapsed descending colon (arrow). Signs of fecal reflux can be appreciated besides the gall-bladder (dash arrow) accounting for the mottled appearance depicted in the sub-hepatic space on the plain film series (B). On the coronal plane (B), the cecum (ce) appears tilted in the sub-hepatic space as it can be appreciated by the location of the terminal ileum (arrowhead) which also exhibits signs of fecal reflux, dash arrows indicate gas bubbles at the level of the hepatic hilum.
- Citation: Camera L, Calabrese M, Mainenti PP, Masone S, Vecchio WD, Persico G, Salvatore M. Volvulus of the ascending colon in a non-rotated midgut: Plain film and MDCT findings. World J Radiol 2012; 4(10): 439-442
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1949-8470/full/v4/i10/439.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4329/wjr.v4.i10.439