Copyright
©2012 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
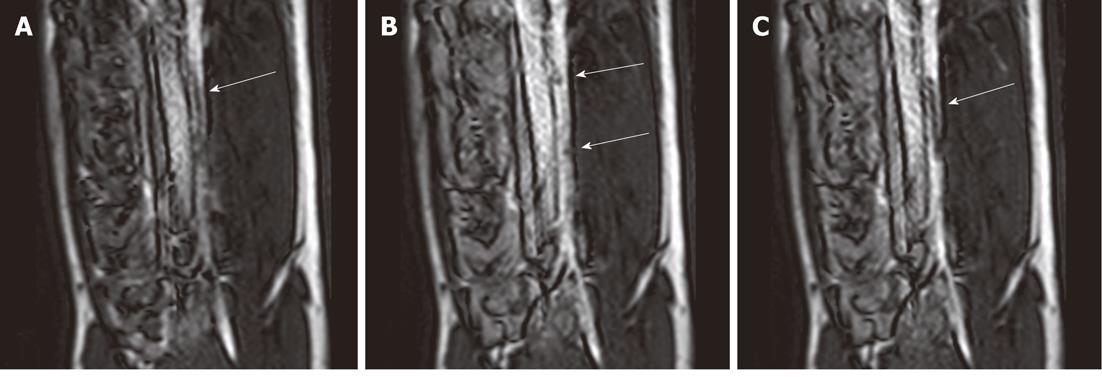
Figure 1 Selected magnetic resonance-guided images of the abdominal aorta prior to the administration of intravascular gadolinium-based (T1 enhancing agent) magnetic resonance contrast medium, the inflated balloon on the catheter is evident (arrow), but suffers substantial downstream signal loss (A).
After a blood pool magnetic resonance (MR) contrast medium administration (B), the MR dysprosium-chelate (markers placed on the catheter shaft) becomes evident (arrows, B) and, following inflation, the spatial extent of the balloon is better delineated (arrow, C).
- Citation: Saeed M, Wilson M. Value of MR contrast media in image-guided body interventions. World J Radiol 2012; 4(1): 1-12
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1949-8470/full/v4/i1/1.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4329/wjr.v4.i1.1