Copyright
©2011 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Radiol. Dec 28, 2011; 3(12): 298-305
Published online Dec 28, 2011. doi: 10.4329/wjr.v3.i12.298
Published online Dec 28, 2011. doi: 10.4329/wjr.v3.i12.298
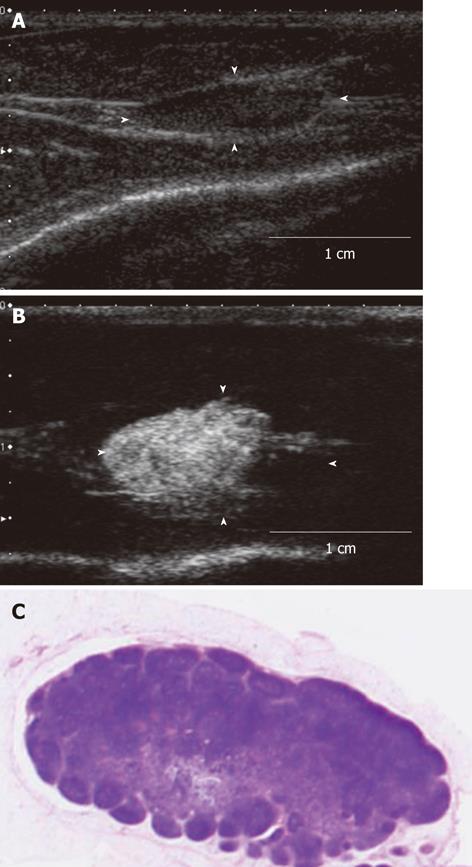
Figure 4 The contrast-enhanced ultrasonography image and histopathological image of the acute inflammation-induced lymph node enlargement model.
The model of inflammation-induced lymph node enlargement at 7 d after Escherichia coli was implanted (model 9). A: The enlarged popliteal lymph node with a diameter of 13 mm that was seen in the B mode ultrasound image. This lymph node showed up as a hypoechoic mass; B: Image of the popliteal lymph node that was imaged after the contrast agent was administered in the periphery of the primary lesion. The entire lymph node was imaged; C: Histopathological image (hematoxylin-eosin stain) of the lymph node that was extracted. Invasion of inflammatory cells, mainly nucleocytes, was seen. These are findings of acute lymphadenitis.
- Citation: Aoki T, Moriyasu F, Yamamoto K, Shimizu M, Yamada M, Imai Y. Image of tumor metastasis and inflammatory lymph node enlargement by contrast-enhanced ultrasonography. World J Radiol 2011; 3(12): 298-305
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1949-8470/full/v3/i12/298.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4329/wjr.v3.i12.298