Copyright
©2011 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Radiol. Nov 28, 2011; 3(11): 273-278
Published online Nov 28, 2011. doi: 10.4329/wjr.v3.i11.273
Published online Nov 28, 2011. doi: 10.4329/wjr.v3.i11.273
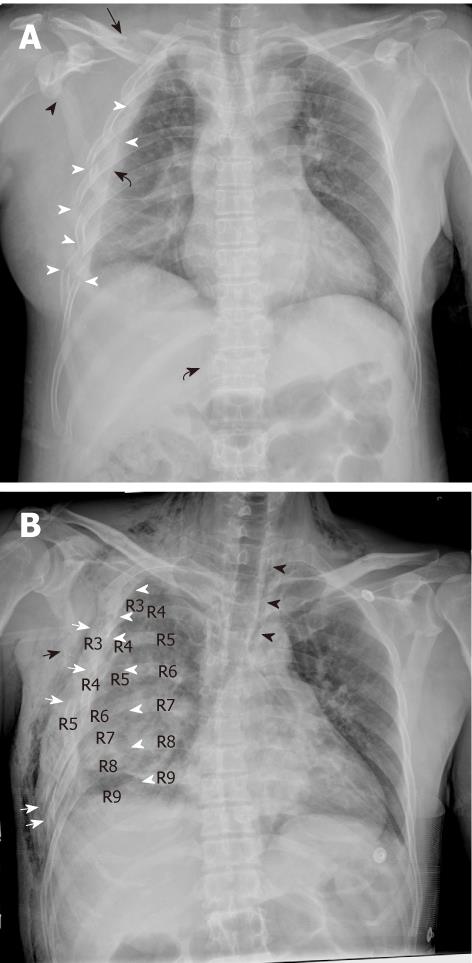
Figure 1 An antero-posterior chest digital radiograph of patients who suffered crush injury in the Sichuan earthquake.
A: Chest digital radiography (CDR) shows the right-sided 2-8 rib fractures at lateral sites (white arrow head), and non-rib thoracic fractures including clavicle (black arrow), scapula (black arrow head) and T12 vertebral body (sinistrad black curved arrow) in a 56-year-old woman after 4 d. Right-sided hemothorax (dextrad black curved arrow) and parenchymal contusion are noted; B: CDR shows thoracic cage asymmetry due to right-sided 3-7 rib fractures and severe dislocations at posterior sites (white arrow head) and lateral sites (white arrow) causing flail chest in a 51-year-old man after 3 d. Right-sided 8 and 9 rib fractures at posterior sites (white arrow head), scapula fracture (black arrow), hemothorax, pneumomediastium (black arrow head) and parenchymal contusion are shown. Note the widespread subcutaneous emphysema.
- Citation: Dong ZH, Shao H, Chen TW, Chu ZG, Deng W, Tang SS, Chen J, Yang ZG. Digital radiography of crush thoracic trauma in the Sichuan earthquake. World J Radiol 2011; 3(11): 273-278
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1949-8470/full/v3/i11/273.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4329/wjr.v3.i11.273