Copyright
©2010 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Radiol. Aug 28, 2010; 2(8): 298-308
Published online Aug 28, 2010. doi: 10.4329/wjr.v2.i8.298
Published online Aug 28, 2010. doi: 10.4329/wjr.v2.i8.298
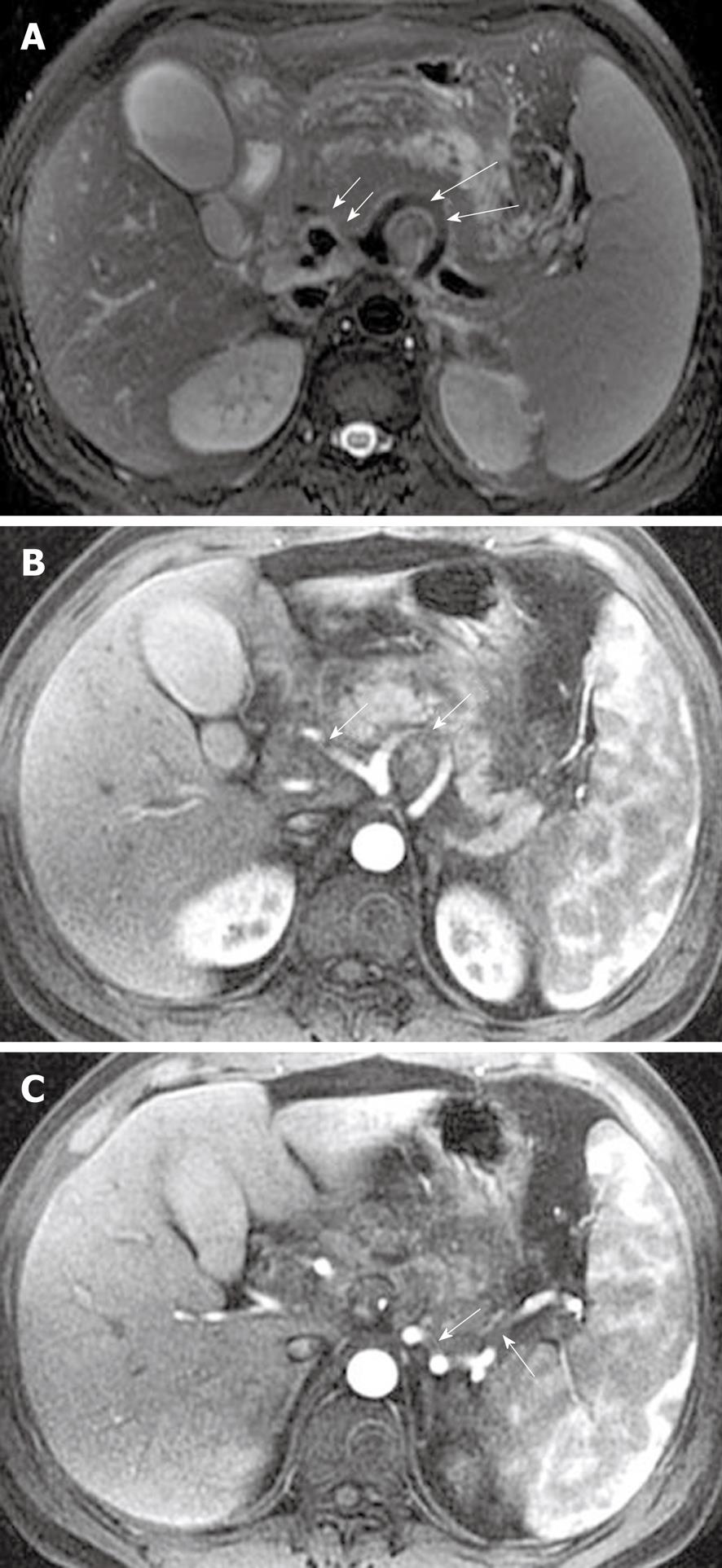
Figure 17 Artery involvement and vasculitis in a 30-year-old man after an episode of acute pancreatitis.
A: Axial magnetic resonance T2-weighted with fat-suppression image shows the loss of vascular flow voiding effect of the involved parts of the common hepatic artery (small arrows) and splenic artery (large arrows); B, C: Axial contrast-enhanced T1-weighted images obtained in arterial phase reveal the poor enhancement of the involved parts of these arteries (arrows) associated with the obscure and rough edges.
- Citation: Xiao B, Zhang XM. Magnetic resonance imaging for acute pancreatitis. World J Radiol 2010; 2(8): 298-308
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1949-8470/full/v2/i8/298.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4329/wjr.v2.i8.298