Copyright
©2010 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Radiol. Aug 28, 2010; 2(8): 298-308
Published online Aug 28, 2010. doi: 10.4329/wjr.v2.i8.298
Published online Aug 28, 2010. doi: 10.4329/wjr.v2.i8.298
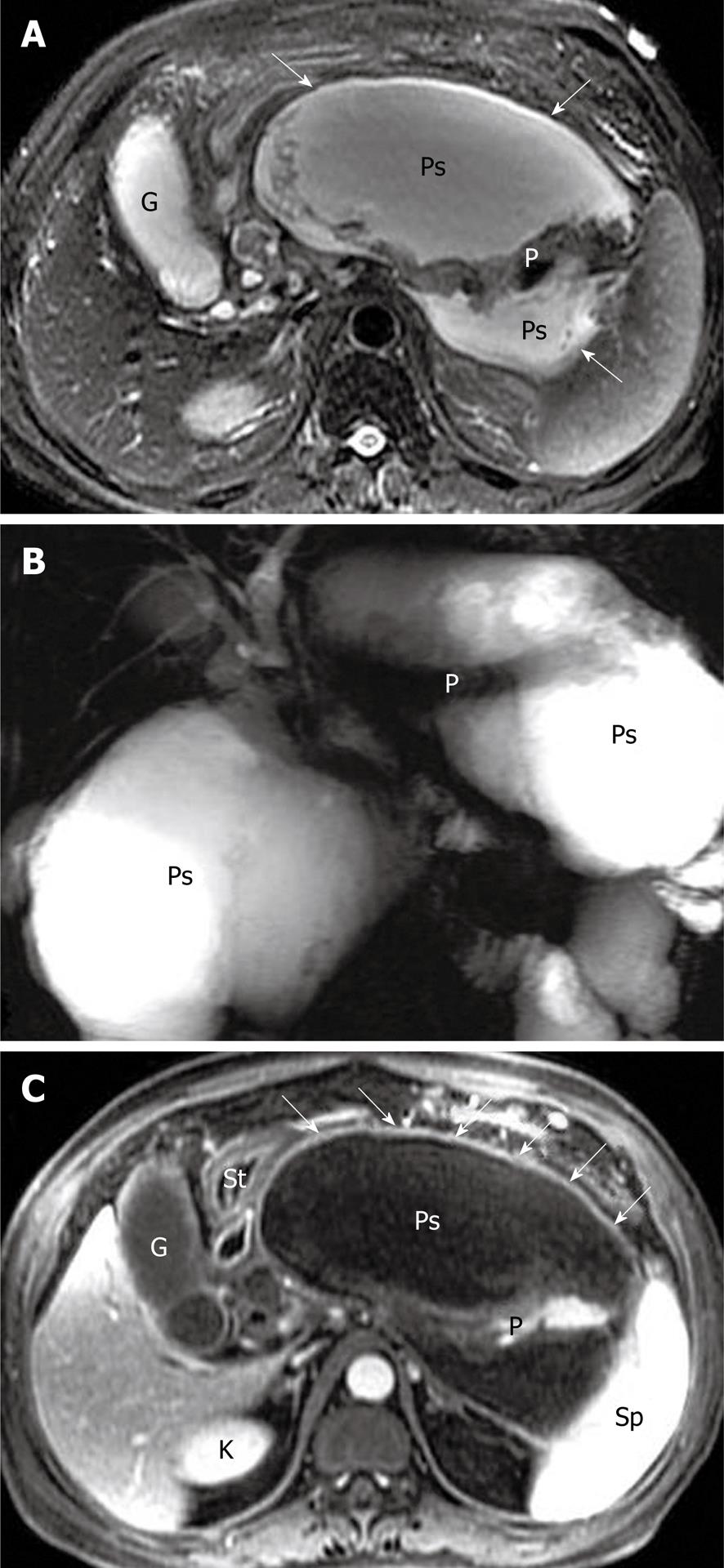
Figure 13 A large peripancreatic pseudocyst in a 41-year-old man who present as abdominal distension after acute post-necrotic pancreatitis.
Axial magnetic resonance (MR) T2-weighted with fat-suppression image (A) and MR cholangiopancreatography (B) show a large pseudocyst (arrows) with homogeneous hypersignal intensity around the pancreas. Axial T1-weighted image obtained with intravenous contrast material (C) reveals the enhancement of the thick wall (arrows) of the pseudocyst. The extrusion and displacement of the stomach (St) is seen due to the tension of the pseudocyst. G: Gallbladder; P: Pancreas; Ps: Pseudocyst; K: Kidney; Sp: Spleen; St: Stomach.
- Citation: Xiao B, Zhang XM. Magnetic resonance imaging for acute pancreatitis. World J Radiol 2010; 2(8): 298-308
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1949-8470/full/v2/i8/298.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4329/wjr.v2.i8.298