Copyright
©2010 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Radiol. Aug 28, 2010; 2(8): 298-308
Published online Aug 28, 2010. doi: 10.4329/wjr.v2.i8.298
Published online Aug 28, 2010. doi: 10.4329/wjr.v2.i8.298
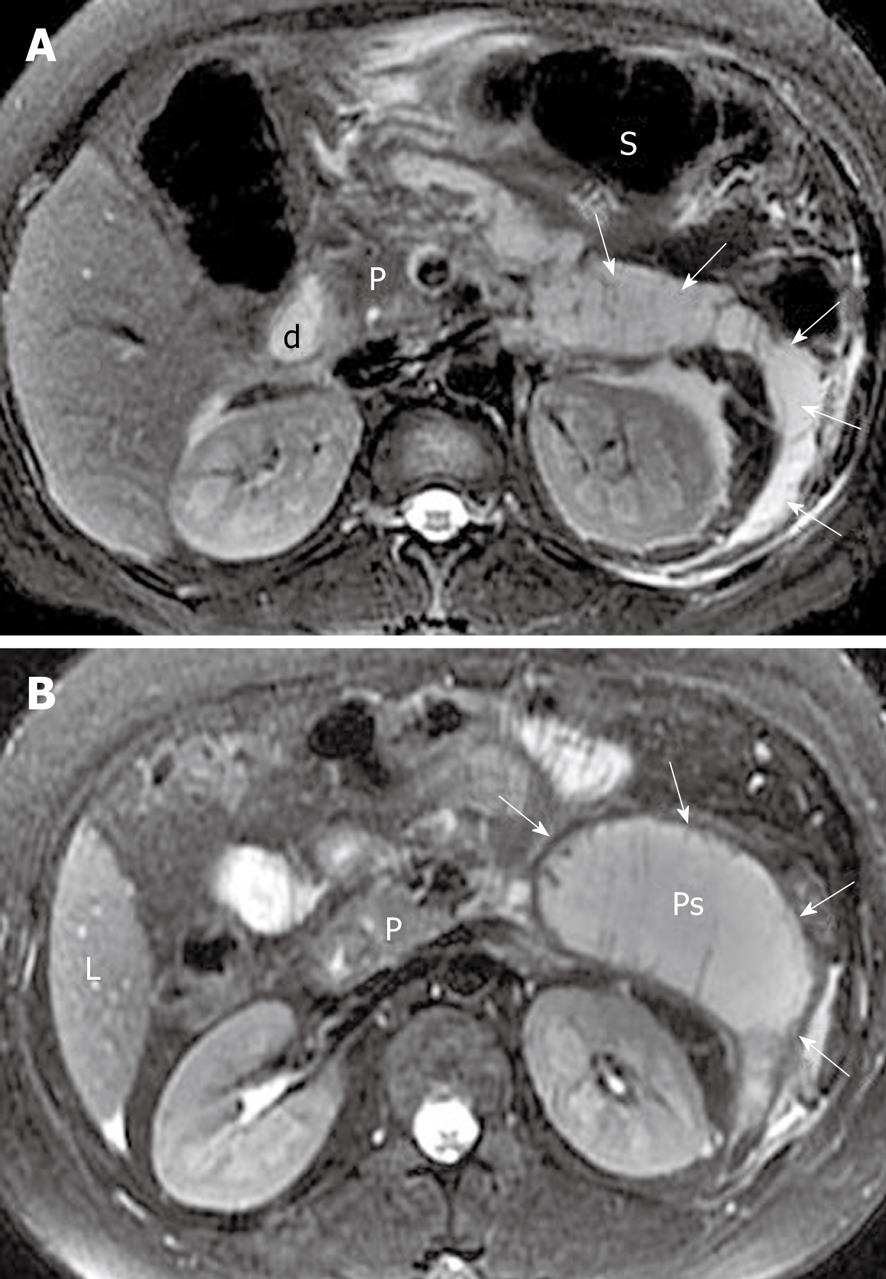
Figure 11 Acute pancreatitis and peripancreatic and retroperitoneal fluid collections in a 42-year-old man.
A: Axial magnetic resonance T2-weighted with fat-suppression image obtained at the time of hospital admission shows large heterogeneous fluid collections (arrows) associated with areas of tissue liquified necrosis in the pararenal space of the left kidney; B: Follow-up axial T2-weighted with fat-suppression image reveals an encapsulated fluid collection (arrows) in the process of the development of a pseudocyst. L: Liver; P: Pancreas; S: Stomach; d: Duodenal bulb; Ps: Pseudocyst.
- Citation: Xiao B, Zhang XM. Magnetic resonance imaging for acute pancreatitis. World J Radiol 2010; 2(8): 298-308
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1949-8470/full/v2/i8/298.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4329/wjr.v2.i8.298