Copyright
©2010 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Radiol. Apr 28, 2010; 2(4): 122-134
Published online Apr 28, 2010. doi: 10.4329/wjr.v2.i4.122
Published online Apr 28, 2010. doi: 10.4329/wjr.v2.i4.122
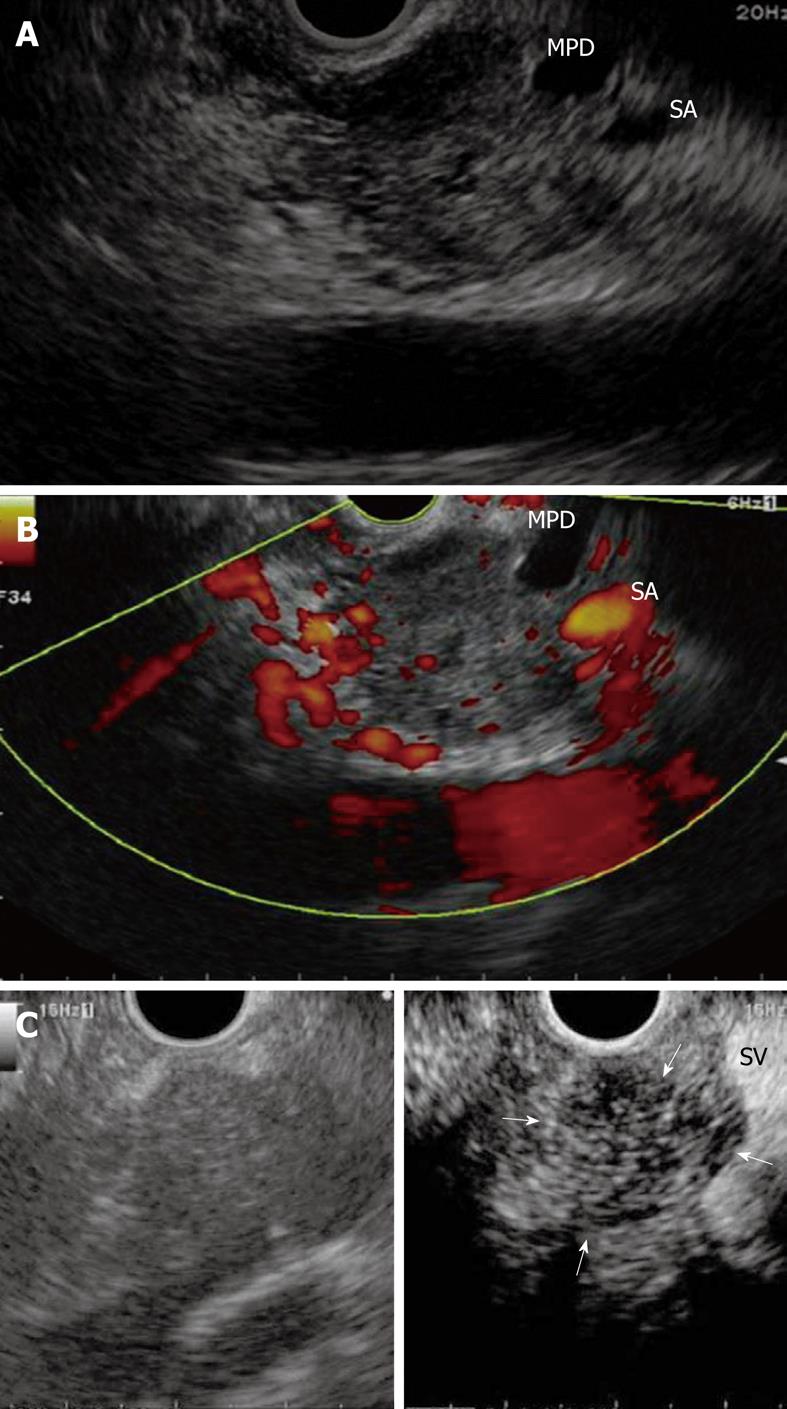
Figure 11 Pancreatic adenocarcinoma.
A: EUS shows a heterogeneous hypoechoic mass with irregular margins at the body of the pancreas and tail side main pancreatic duct enlarged due to the infiltrating mass; B: Contrast-enhanced power Doppler EUS shows a hypovascular nodule compared with the surrounding pancreatic tissue; C: Contrast-enhanced harmonic EUS showing a clear margin and hypovascular nodule compared with surrounding pancreatic tissue (arrows) without blooming artifact such as that found with Doppler imaging. Left: B-mode imaging; Right: Contrast imaging. MPD: Main pancreatic duct; SA: Splenic artery.
- Citation: Sakamoto H, Kitano M, Kamata K, El-Masry M, Kudo M. Diagnosis of pancreatic tumors by endoscopic ultrasonography. World J Radiol 2010; 2(4): 122-134
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1949-8470/full/v2/i4/122.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4329/wjr.v2.i4.122