Copyright
©2010 Baishideng.
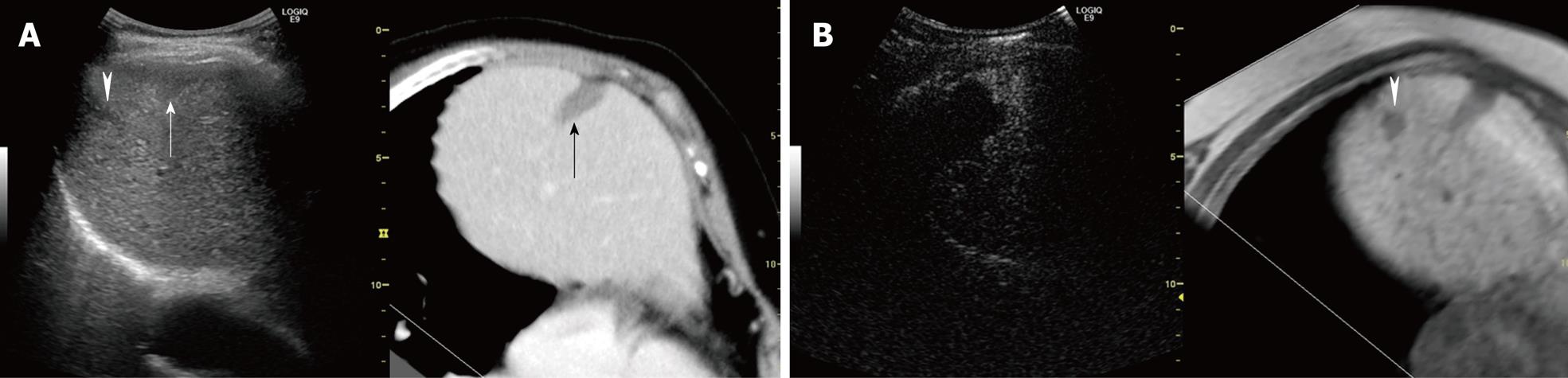
Figure 10 A 77-year-old woman with newly developed HCC (maximum diameter 12 mm) in segment VIII.
A: Fusion image combining arterial phase contrast-enhanced CT (right side) and conventional US (left side). Arterial phase contrast-enhanced CT shows hypo-attenuation area previously treated by RFA alone (arrow). Conventional US shows two hypo-echoic lesions. One is an HCC lesion which was previously treated by RFA (arrow) and the other is a new HCC lesion which was not detectable by dynamic CT (arrowhead); B: Fusion image combining hepatobiliary phase contrast-enhanced MRI with Gd-EOB-DTPA (right side) and middle phase Sonazoid-enhanced US at a low MI (left side). Hepatobiliary phase contrast-enhanced MRI with Gd-EOB-DTPA shows a small hypo-intense area in segment VIII (arrowhead). Middle phase Sonazoid-enhanced US obtained 1 d after RFA shows the tumor as a perfusion defect. This non-enhanced area is larger than the hypo-echoic lesion seen on the hepatobiliary phase contrast-enhanced MRI with Gd-EOB-DTPA. Normal liver parenchyma is enhanced.
- Citation: Numata K, Luo W, Morimoto M, Kondo M, Kunishi Y, Sasaki T, Nozaki A, Tanaka K. Contrast enhanced ultrasound of hepatocellular carcinoma. World J Radiol 2010; 2(2): 68-82
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1949-8470/full/v2/i2/68.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4329/wjr.v2.i2.68