Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Radiol. Feb 28, 2025; 17(2): 102373
Published online Feb 28, 2025. doi: 10.4329/wjr.v17.i2.102373
Published online Feb 28, 2025. doi: 10.4329/wjr.v17.i2.102373
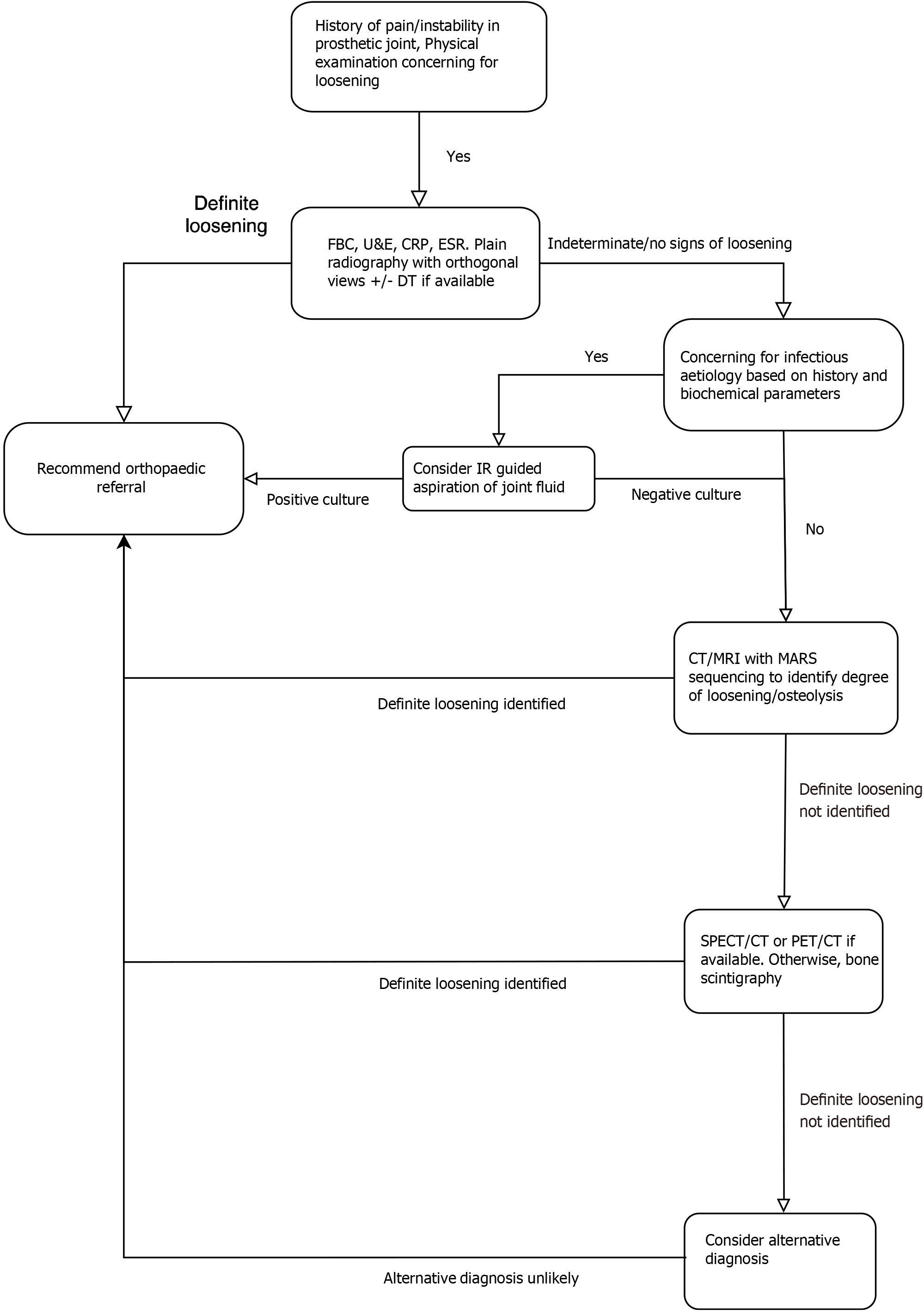
Figure 5 Summary flow diagram of recommended radiological diagnostic pathway.
The flow diagram above aims to aid the general radiologist in the diagnosis of suspected periprosthetic loosening. As with any most pathologies, the pathway begins with careful history taking and physical examination by the referring clinician. Baseline biochemical markers and plain radiography ± digital tomosynthesis form the first step in the diagnostic pathway. The recommended further steps are based on the results of the initial step and are listed above. Discussion with the clinician who is the primary carer for the patient is crucial in every step of the pathway. FBC: Full blood count; U&E: Urea and electrolytes; CRP: C reactive protein; ESR: Erythrocyte sedimentation rate; IR: Interventional radiology; DT: Digital tomosynthesis; CT: Computed tomography; MRI: Magnetic resonance imaging; MARS: Metal artefact reduction sequence; SPECT: Single-photon emission computed tomography; PET: Positron emission tomography.
- Citation: Shet SS, Kakish E, Murphy SC, Roopnarinesingh R, Power SP, Maher MM, Ryan DJ. Imaging evaluation of periprosthetic loosening: A primer for the general radiologist. World J Radiol 2025; 17(2): 102373
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1949-8470/full/v17/i2/102373.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4329/wjr.v17.i2.102373