Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Radiol. Feb 28, 2025; 17(2): 102373
Published online Feb 28, 2025. doi: 10.4329/wjr.v17.i2.102373
Published online Feb 28, 2025. doi: 10.4329/wjr.v17.i2.102373
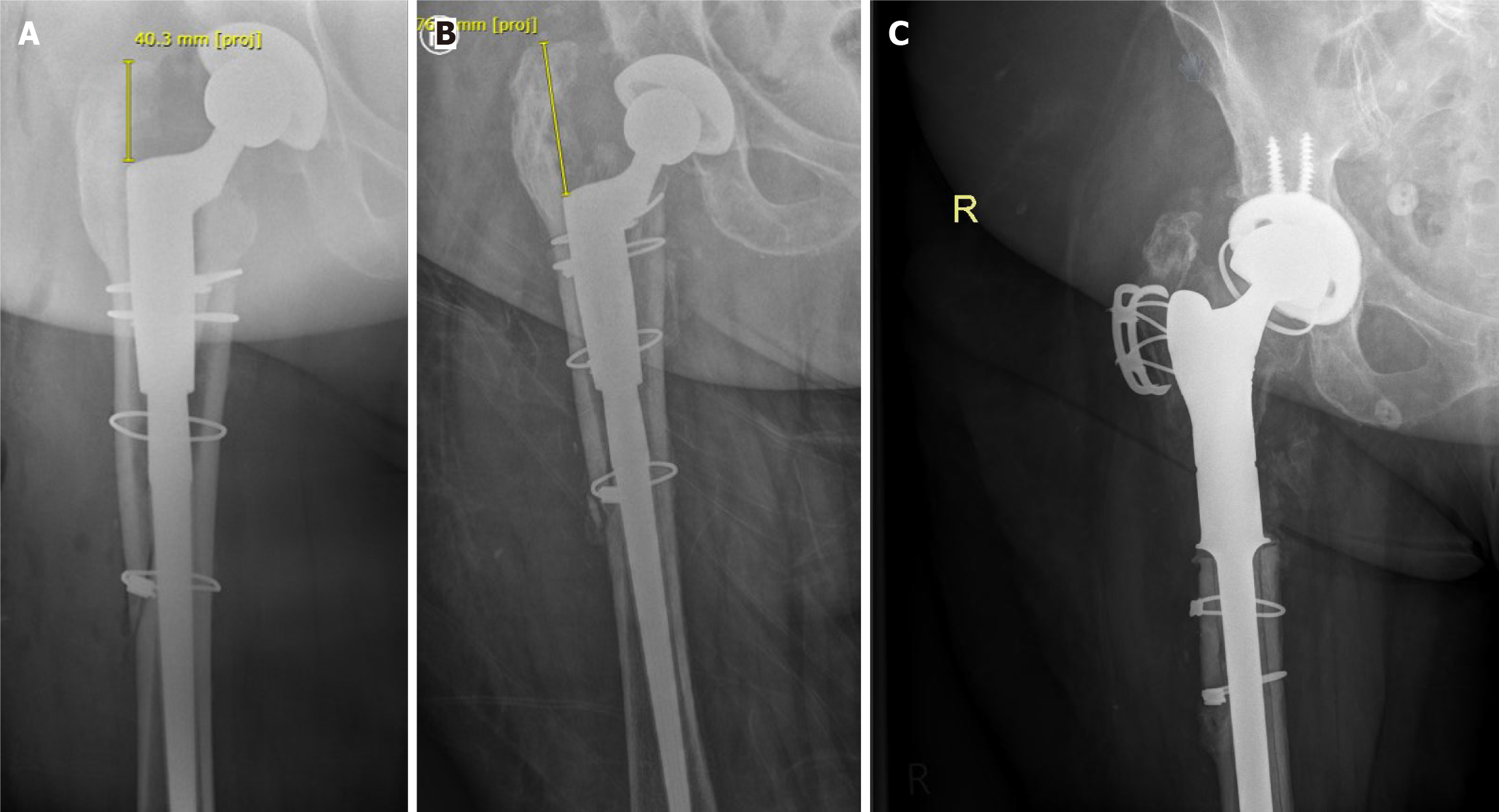
Figure 1 Subsidence of a loose femoral component in a revision total hip arthroplasty.
The above case showcases the utilisation of plain radiography in the diagnosis of aseptic loosening. This patient had presented to the outpatient’s clinic 1 year following revision total hip arthroplasty with complaints of right sided hip pain that was gradually worsening. The revision surgery utilised a diaphyseal bearing modular revision system with cerclage cables for closure of the proximal femoral osteotomy as a result of periprosthetic fracture. A–C: Immediate postoperative (A) and 1-year postoperative (B) plain radiographs are displayed with significant subsidence of the femoral component noted in the follow-up appointment. Following careful clinical evaluation and confirmation of normal biochemical markers, the patient was diagnosed with aseptic loosening and underwent a planned revision total hip arthroplasty with a proximal femoral replacement (C).
- Citation: Shet SS, Kakish E, Murphy SC, Roopnarinesingh R, Power SP, Maher MM, Ryan DJ. Imaging evaluation of periprosthetic loosening: A primer for the general radiologist. World J Radiol 2025; 17(2): 102373
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1949-8470/full/v17/i2/102373.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4329/wjr.v17.i2.102373