Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Radiol. Aug 28, 2024; 16(8): 294-316
Published online Aug 28, 2024. doi: 10.4329/wjr.v16.i8.294
Published online Aug 28, 2024. doi: 10.4329/wjr.v16.i8.294
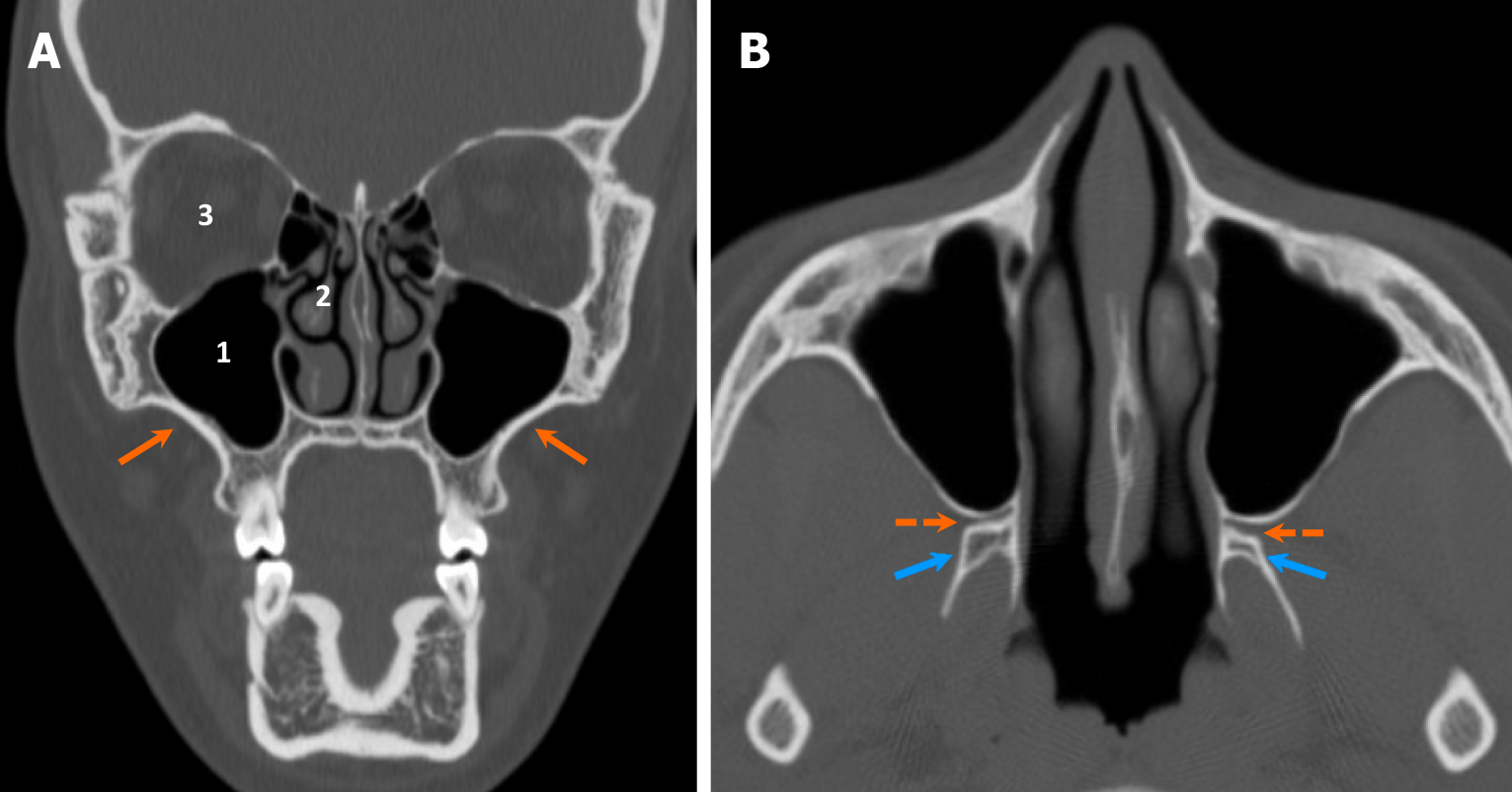
Figure 2 Anatomy of the maxilla.
A and B: Coronal (A) and axial (B) computed tomography images demonstrate the normal anatomy of the maxilla, which forms the midface (orange arrows), along with related structures: (1) Maxillary sinuses located centrally; (2) Nasal cavity located medially; and (3) Orbits located superiorly. The pterygopalatine fossae (dashed arrows) are situated between the maxillary sinuses and the pterygoid processes of the sphenoid bone (blue arrows), serving as an important location for the pterygopalatine ganglion (CN V2).
- Citation: Choi WJ, Lee P, Thomas PC, Rath TJ, Mogensen MA, Dalley RW, Wangaryattawanich P. Imaging approach for jaw and maxillofacial bone tumors with updates from the 2022 World Health Organization classification. World J Radiol 2024; 16(8): 294-316
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1949-8470/full/v16/i8/294.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4329/wjr.v16.i8.294