Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Radiol. Dec 28, 2024; 16(12): 722-748
Published online Dec 28, 2024. doi: 10.4329/wjr.v16.i12.722
Published online Dec 28, 2024. doi: 10.4329/wjr.v16.i12.722
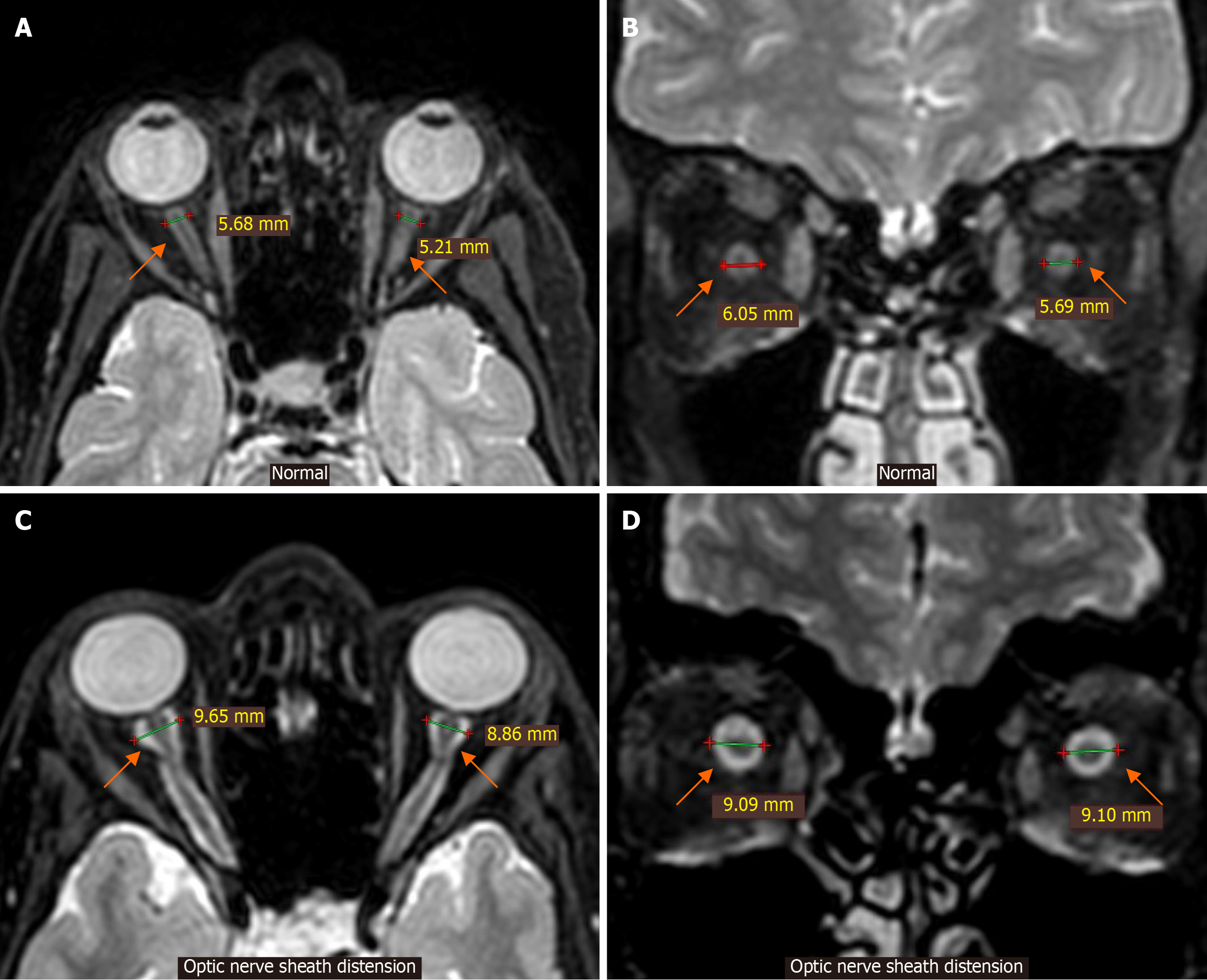
Figure 8 Optic nerve sheath distension.
A and B: Axial (A) and coronal T2-weighted magnetic resonance images (B) at the level of the globes and optic nerves in a patient with no idiopathic intracranial hypertension signs or symptoms are provided for reference. Note the normal caliber and diameter of the optic nerve sheaths (arrows); C and D: Axial (C) and coronal T2-weighted magnetic resonance images (D) at the level of the globes and optic nerves in a patient with signs and symptoms of idiopathic intracranial hypertension demonstrate increased caliber of the optic nerve sheaths (arrows) (diameter > 8-9 mm) as a result of cerebrospinal fluid distension.
- Citation: Arkoudis NA, Davoutis E, Siderakis M, Papagiannopoulou G, Gouliopoulos N, Tsetsou I, Efthymiou E, Moschovaki-Zeiger O, Filippiadis D, Velonakis G. Idiopathic intracranial hypertension: Imaging and clinical fundamentals. World J Radiol 2024; 16(12): 722-748
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1949-8470/full/v16/i12/722.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4329/wjr.v16.i12.722