Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Radiol. Nov 28, 2024; 16(11): 668-677
Published online Nov 28, 2024. doi: 10.4329/wjr.v16.i11.668
Published online Nov 28, 2024. doi: 10.4329/wjr.v16.i11.668
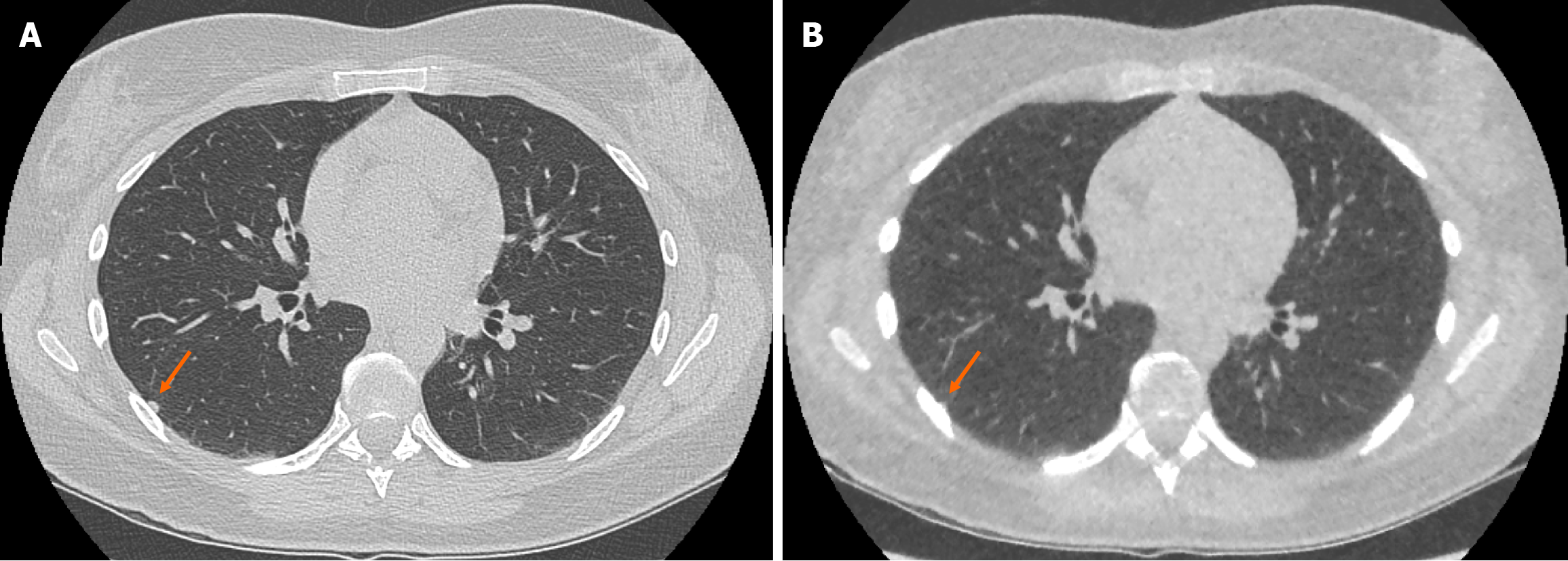
Figure 4 Example of false negative pulmonary nodule identification on ultra-low-dose computed tomography chest.
A: Selected axial slice of a standard dose computed tomography (CT) chest presented in lung windows with a solid pulmonary nodule abutting the pleura in the lateral segment of the right lower lobe (arrow); B: Selected axial slice of an ultra-low dose CT chest with model-based iterative reconstruction in the same patient at the same level presented in lung windows demonstrating the less conspicuous pulmonary nodule that was not identified (arrow). The incidence of false negative solid nodule identification was minimal and did not reach statistical significance.
- Citation: O'Regan PW, Harold-Barry A, O'Mahony AT, Crowley C, Joyce S, Moore N, O'Connor OJ, Henry MT, Ryan DJ, Maher MM. Ultra-low-dose chest computed tomography with model-based iterative reconstruction in the analysis of solid pulmonary nodules: A prospective study. World J Radiol 2024; 16(11): 668-677
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1949-8470/full/v16/i11/668.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4329/wjr.v16.i11.668