Copyright
©The Author(s) 2023.
World J Radiol. Jun 28, 2023; 15(6): 157-169
Published online Jun 28, 2023. doi: 10.4329/wjr.v15.i6.157
Published online Jun 28, 2023. doi: 10.4329/wjr.v15.i6.157
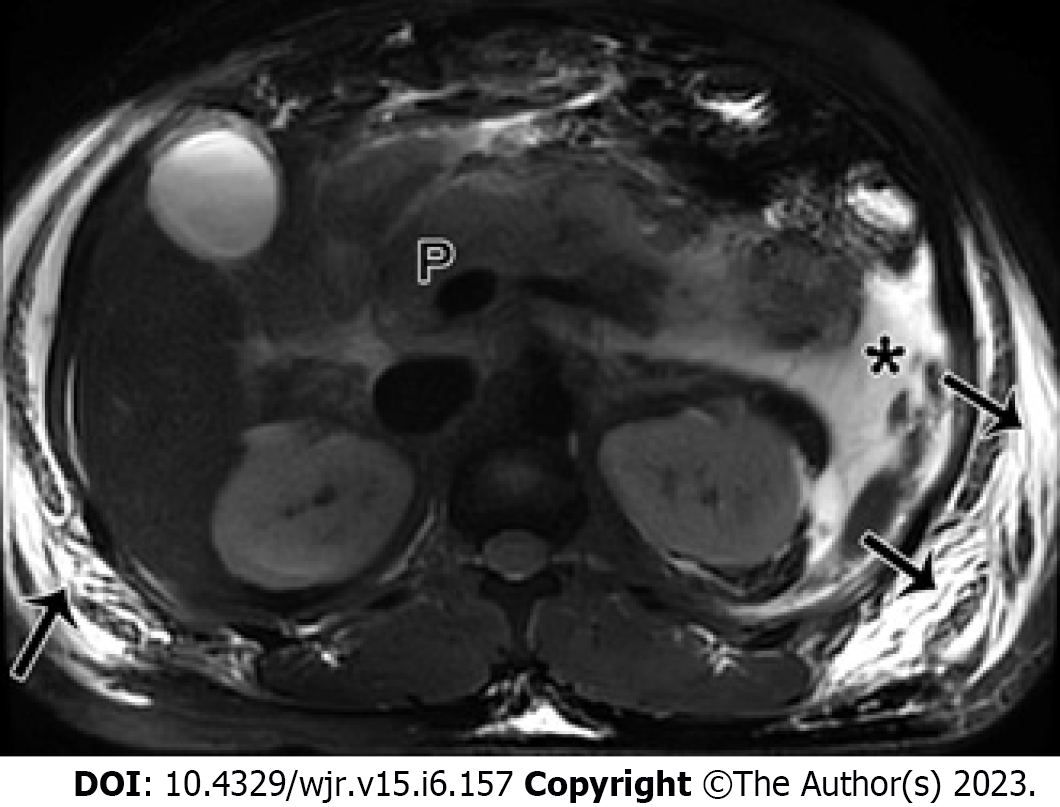
Figure 5 Acute pancreatitis can also cause subcutaneous edema and fluid collection changes in the abdominal walls.
A 25-year-old man with acute necrotizing pancreatitis and acute necrotic collection accompanied by conspicuous subcutaneous edema. Magnetic resonance imaging fat-suppressed T1-weighted imaging shows a majority of hyperintense fluid collections (*) in the left pararenal anterior space, and large flaps of hyperintense changes (arrows) in subcutaneous tissues of bilateral flanks and abdominal walls. P: Pancreas.
- Citation: Song LJ, Xiao B. Acute pancreatitis: Structured report template of magnetic resonance imaging. World J Radiol 2023; 15(6): 157-169
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1949-8470/full/v15/i6/157.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4329/wjr.v15.i6.157