Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Radiol. Jul 28, 2022; 14(7): 194-208
Published online Jul 28, 2022. doi: 10.4329/wjr.v14.i7.194
Published online Jul 28, 2022. doi: 10.4329/wjr.v14.i7.194
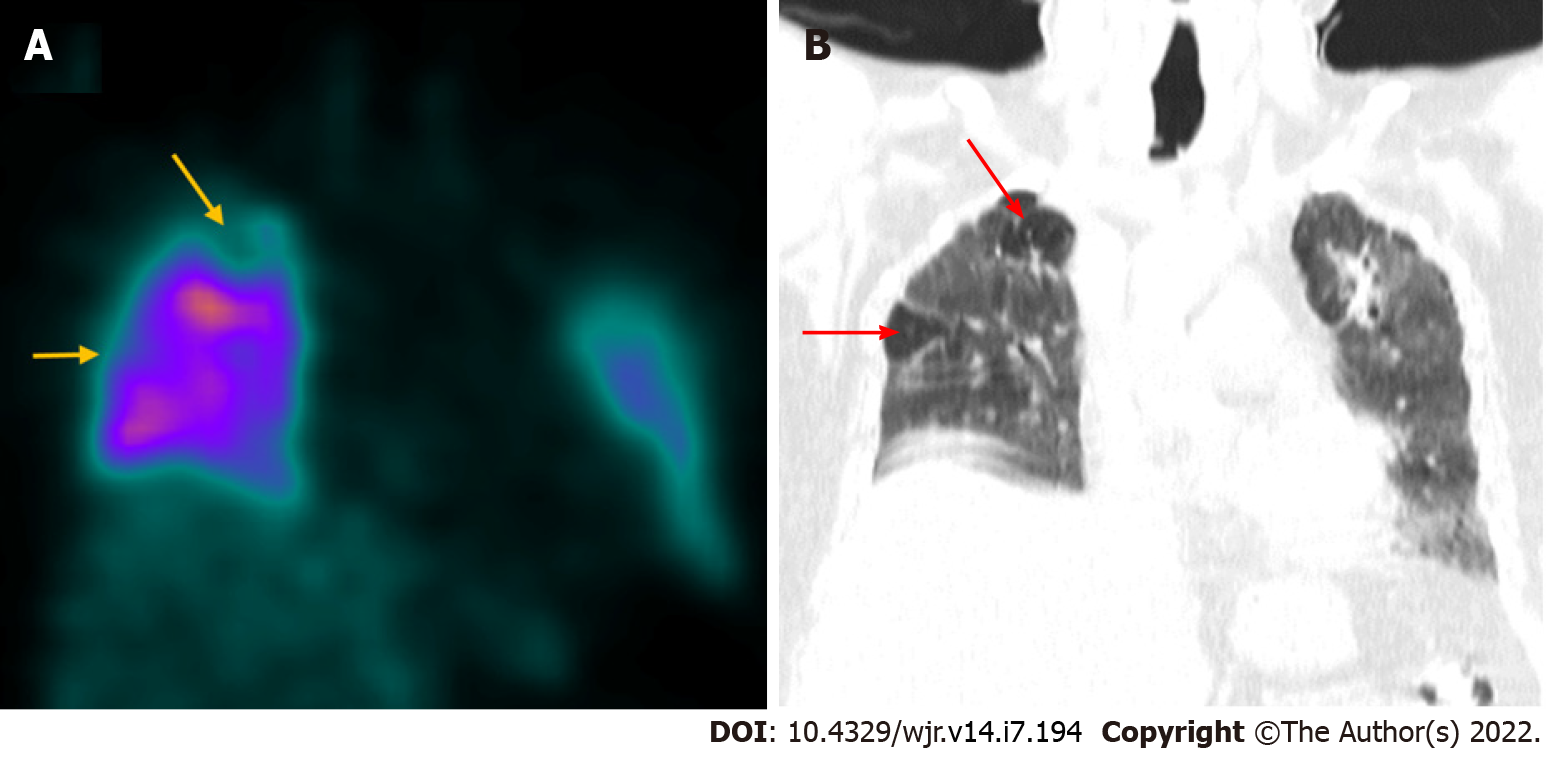
Figure 2 Coronavirus disease 2019 related pulmonary thromboembolism.
A 60-year-old male with history of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) infection 2 mo ago underwent Tc-99m macro-aggregated albumin lung perfusion imaging to rule out pulmonary thromboembolism. A: Coronal SPECT images show reduced tracer uptake (yellow arrows) in sub-segmental defects involving the right lung apex and the lateral segment of the RML; B: Corresponding coronal CT image shows relatively normal lung parenchyma (red arrows) in the above-mentioned sites (mismatched defects) suggestive of pulmonary thromboembolism. The rest of the lung parenchyma shows ground glass changes, fibrotic bands, and bronchiectatic changes consistent with post-COVID recovery phase.
- Citation: Chandekar KR, Satapathy S, Singh H, Bhattacharya A. Molecular imaging as a tool for evaluation of COVID-19 sequelae – A review of literature. World J Radiol 2022; 14(7): 194-208
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1949-8470/full/v14/i7/194.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4329/wjr.v14.i7.194