Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Radiol. Feb 28, 2022; 14(2): 30-46
Published online Feb 28, 2022. doi: 10.4329/wjr.v14.i2.30
Published online Feb 28, 2022. doi: 10.4329/wjr.v14.i2.30
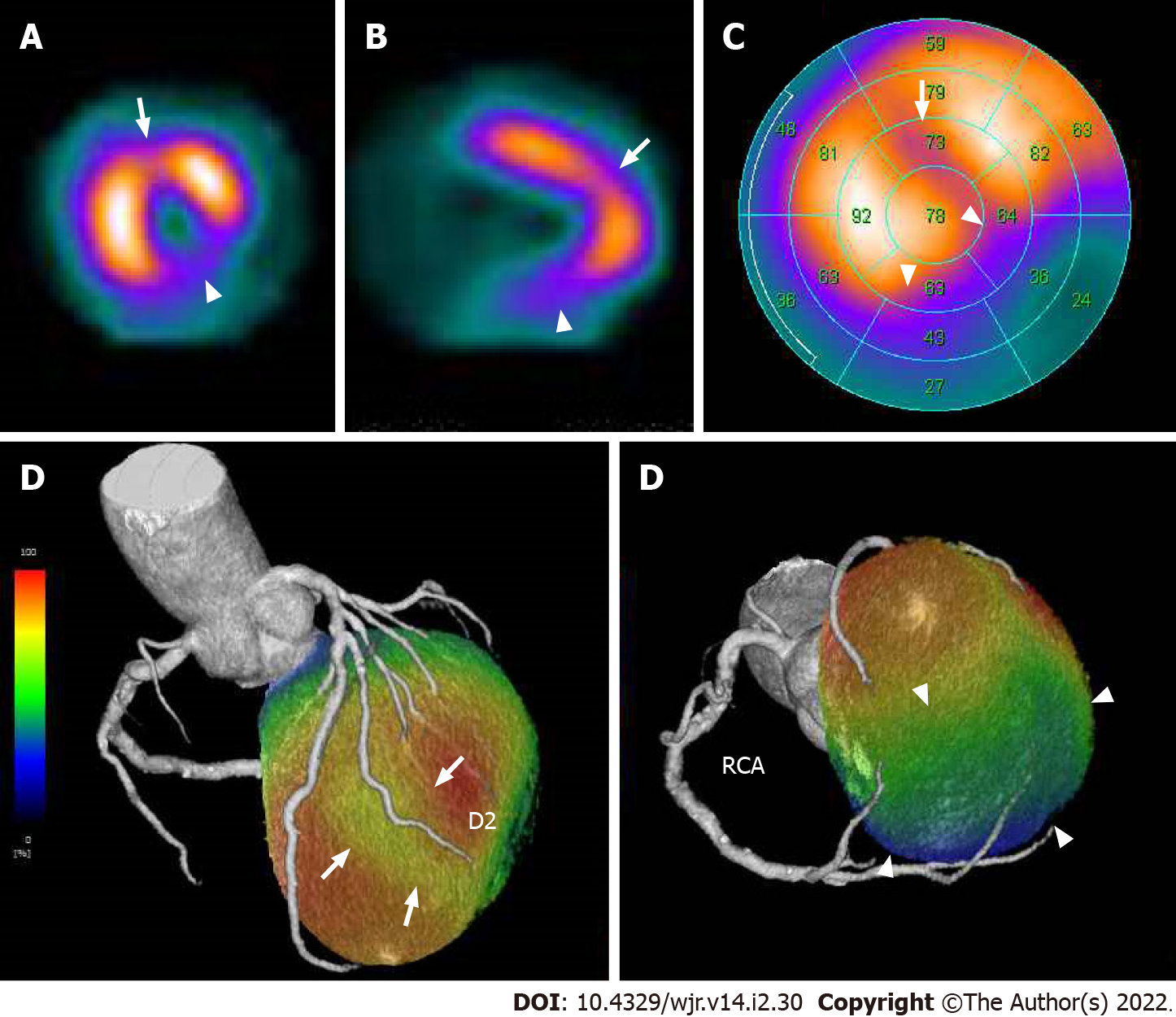
Figure 19 Corresponding sestamibi single-photon emission computed tomography in acute coronary syndrome of right coronary artery complicated with anterior old myocardial infarction.
Same patient as Figures 17 and 18. Rest technetium-99m sestamibi single-photon emission computed tomography (SPECT) myocardial perfusion imaging (MPI) are shown. Short axis (A) and vertical long axis (B) views and a bull’s eye polar plot (C) of rest technetium-99m sestamibi SPECT MPI showed perfusion defects in the basal to mid inferior, inferolateral, and inferoseptal walls of the left ventricle (arrowheads). In addition, SPECT MPI also showed hypoperfusion in the mid anterior wall of the left ventricle (arrows). The volume-rendered, coregistered SPECT MPI, and cardiac CT images demonstrated that hypoperfusion in the mid anterior wall of the left ventricle seen on the SPECT MPI corresponded with the territory of the second diagonal branch (D, arrows), whereas the perfusion defects in the basal to mid inferior, inferolateral, and inferoseptal walls of the left ventricle seen on the SPECT MPI corresponded with the territory of the right coronary artery (D, arrowheads). LAD: Left anterior descending artery, D2: Second diagonal branch; RCA: Right coronary artery.
- Citation: Yoshihara S. Acute coronary syndrome on non-electrocardiogram-gated contrast-enhanced computed tomography. World J Radiol 2022; 14(2): 30-46
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1949-8470/full/v14/i2/30.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4329/wjr.v14.i2.30