Copyright
©The Author(s) 2020.
World J Radiol. Jun 28, 2020; 12(6): 101-129
Published online Jun 28, 2020. doi: 10.4329/wjr.v12.i6.101
Published online Jun 28, 2020. doi: 10.4329/wjr.v12.i6.101
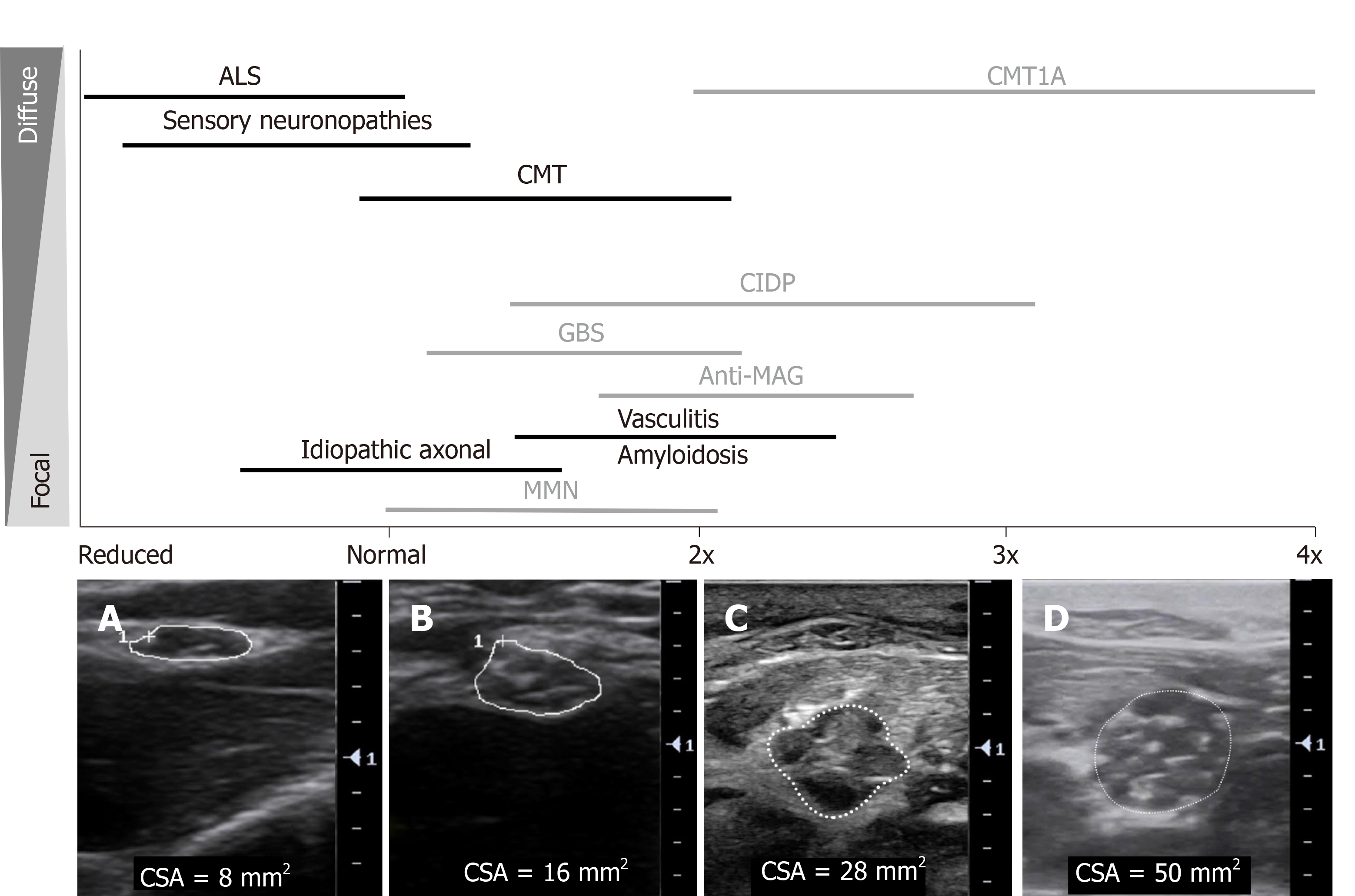
Figure 3 An overview of sonographic findings in inherited and acquired polyneuropathies: degree and distribution of nerve enlargement.
Black: Axonal neuropathies, Grey: Demyelinating neuropathies. Cross-sectional area (CSA) shown in: A: Median nerve at the elbow in a patient with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, CSA 8 mm2; B: Median nerve at the elbow in a healthy control, CSA 16 mm2; C: Median nerve in the forearm in a patient with chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyradiculoneuropathy, CSA 28 mm2, with heterogeneously enlarged, hypoechoic fascicles; D: Median nerve in the forearm in a patient with Charcot Marie Tooth disease type 1A, CSA 50 mm2, with more homogenously enlarged, hypoechoic fascicles. ALS: Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis; CMT1A: Charcot Marie Tooth disease type 1A; CMT: Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease; CIDP: Chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyradiculoneuropathy; GBS: Guillain-Barre syndrome; MAG: Myelin-associated glycoprotein; MMN: Multifocal motor neuropathy; CSA: Cross-sectional area.
- Citation: Carroll AS, Simon NG. Current and future applications of ultrasound imaging in peripheral nerve disorders. World J Radiol 2020; 12(6): 101-129
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1949-8470/full/v12/i6/101.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4329/wjr.v12.i6.101