Copyright
©The Author(s) 2019.
World J Radiol. Mar 28, 2019; 11(3): 27-45
Published online Mar 28, 2019. doi: 10.4329/wjr.v11.i3.27
Published online Mar 28, 2019. doi: 10.4329/wjr.v11.i3.27
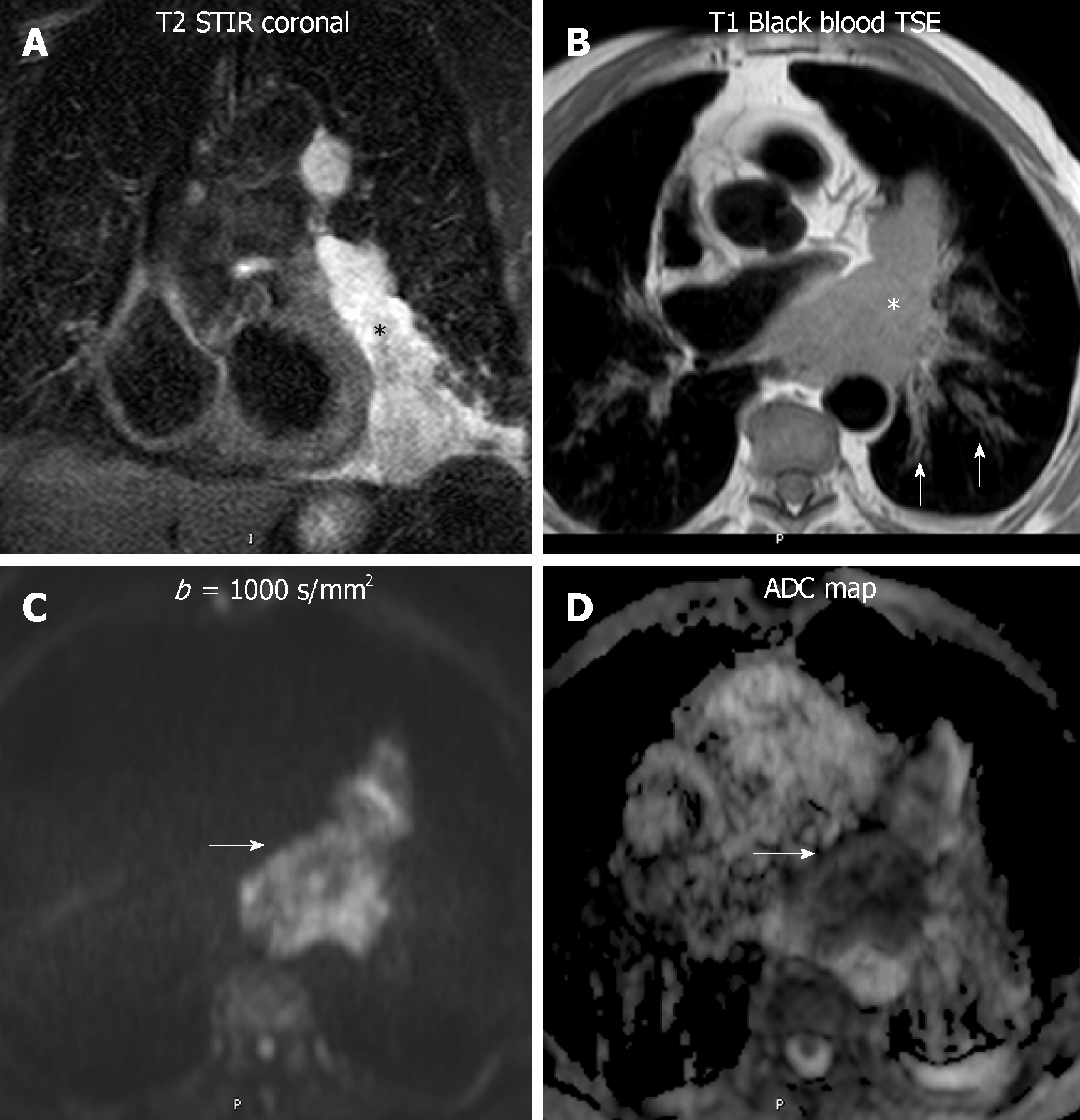
Figure 5 Diffusion weighted imaging of a lymphoma.
An 82 year - old man with a paracardiac lymphomatous mass. A: The lesion is hyperintense in short tau inversion recovery (black asterisk); B: On black blood turbo spin echo T1-weighted image, the lesion is slightly hyperintense compared to striated muscle (white asterisk), with infiltration of the pericardium and hilar vessels. Secondary involvement of the left axial interstitium, bilaterally (white arrows on B); C and D: In high b value diffusion-weighted imaging (b: 1000 s/mm2) the mass showed high signal intensity, with low apparent diffusion coefficient: 1.1 × 10-3 mm2/s on the apparent diffusion coefficient map, in keeping with lymphoma (white arrows on C and D). STIR: Short tau inversion recovery; TSE: Turbo spin echo; ADC: Apparent diffusion coefficient.
- Citation: Broncano J, Alvarado-Benavides AM, Bhalla S, Álvarez-Kindelan A, Raptis CA, Luna A. Role of advanced magnetic resonance imaging in the assessment of malignancies of the mediastinum. World J Radiol 2019; 11(3): 27-45
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1949-8470/full/v11/i3/27.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4329/wjr.v11.i3.27