Copyright
©The Author(s) 2019.
World J Radiol. Mar 28, 2019; 11(3): 27-45
Published online Mar 28, 2019. doi: 10.4329/wjr.v11.i3.27
Published online Mar 28, 2019. doi: 10.4329/wjr.v11.i3.27
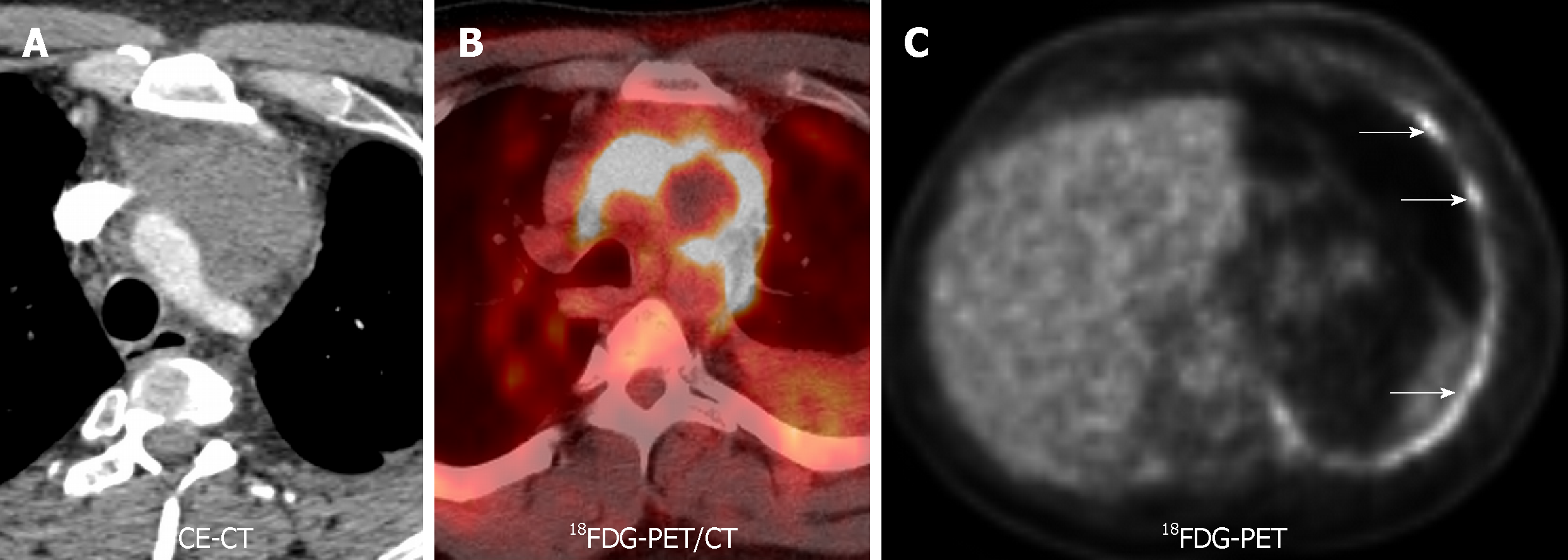
Figure 3 18F-Fluorodeoxiglucose positron emission tomography/computed tomography of a thymic carcinoma.
A 34-year-old with chest pain, found to have infiltrative mass on pulmonary embolism protocol. Pathology revealed a thymic carcinoma. A and B: Contrast-enhanced computed tomography and fused 18F-Fluorodeoxiglucose positron emission tomography/computed tomography showed an 18F-Fluorodeoxiglucose avid anterior mediastinal mass infiltrating thoracic vascular vessels; C: Concentric increased 18F-Fluorodeoxiglucose activity in the left pleura was proven to represent metastatic disease (white arrows). 18F-FDG-PET/CT: 18F-Fluorodeoxiglucose positron emission tomography/computed tomography; 18FDG-PET: 18F-Fluorodeoxiglucose positron emission tomography; CE-CT: Contrast-enhanced computed tomography.
- Citation: Broncano J, Alvarado-Benavides AM, Bhalla S, Álvarez-Kindelan A, Raptis CA, Luna A. Role of advanced magnetic resonance imaging in the assessment of malignancies of the mediastinum. World J Radiol 2019; 11(3): 27-45
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1949-8470/full/v11/i3/27.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4329/wjr.v11.i3.27