Copyright
©The Author(s) 2019.
World J Radiol. Nov 28, 2019; 11(11): 134-143
Published online Nov 28, 2019. doi: 10.4329/wjr.v11.i11.134
Published online Nov 28, 2019. doi: 10.4329/wjr.v11.i11.134
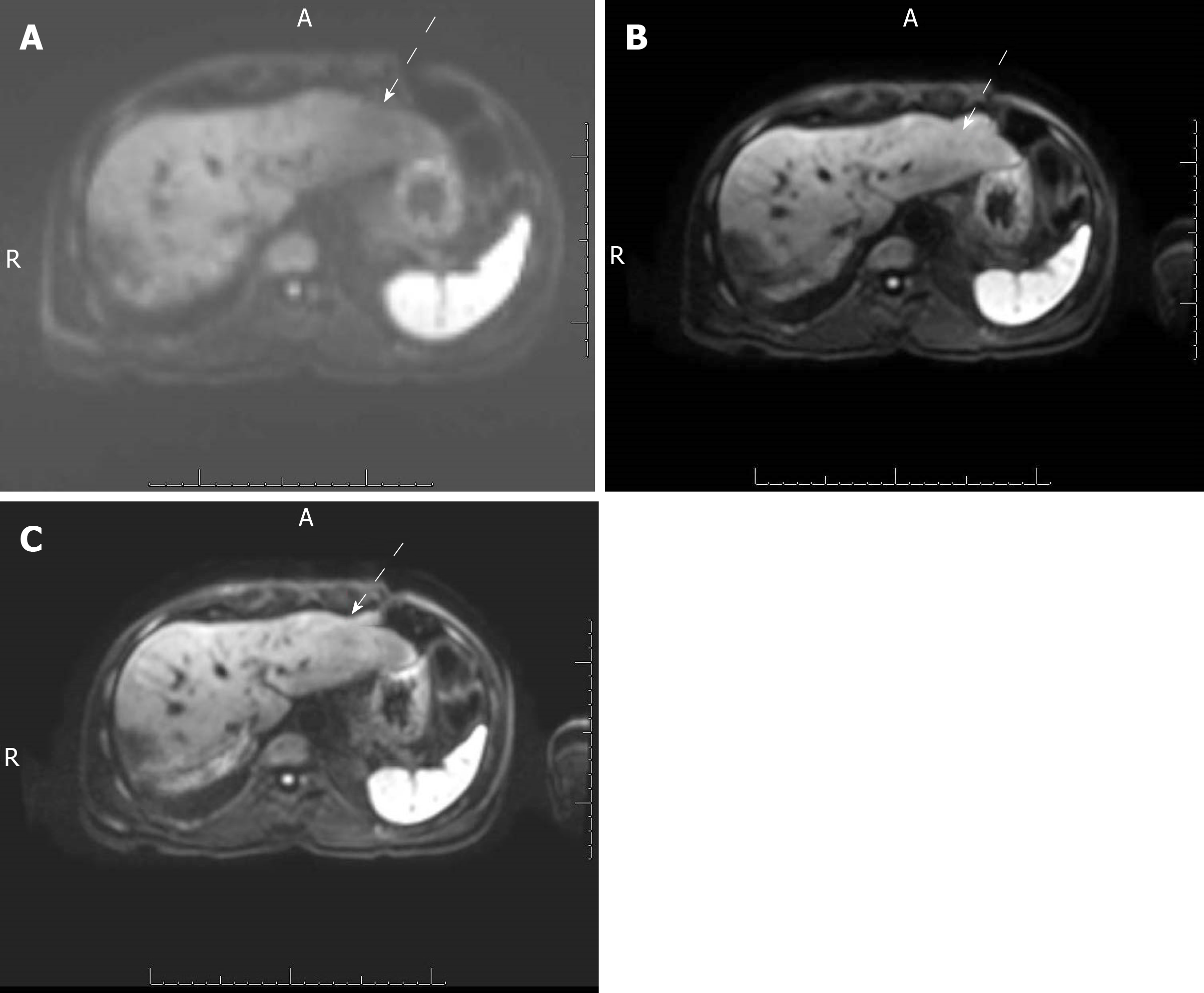
Figure 1 Axial diffusion-weighted images of the liver of a 61-year-old man with a history of hepatocellular carcinoma.
The images were obtained with (A) free-breathing diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI), (B) simultaneous multislice DWI and (C) prospective acquisition correction DWI. The qualitative image quality scores of these series were 3, 5 and 5, respectively. Free-breathing DWI demonstrated artifacts on the left liver, seen as signal loss on the left liver compared to the right liver, (white arrows) that were absent on the other 2 sequences.
- Citation: Szklaruk J, Son JB, Wei W, Bhosale P, Javadi S, Ma J. Comparison of free breathing and respiratory triggered diffusion-weighted imaging sequences for liver imaging. World J Radiol 2019; 11(11): 134-143
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1949-8470/full/v11/i11/134.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4329/wjr.v11.i11.134