Copyright
©The Author(s) 2018.
World J Radiol. Jun 28, 2018; 10(6): 52-64
Published online Jun 28, 2018. doi: 10.4329/wjr.v10.i6.52
Published online Jun 28, 2018. doi: 10.4329/wjr.v10.i6.52
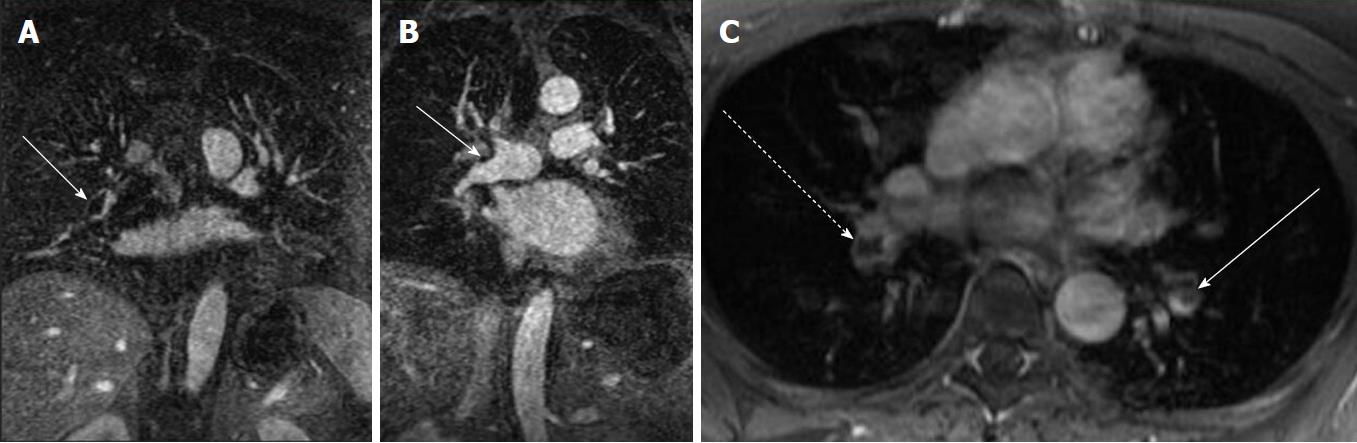
Figure 1 Direct findings of pulmonary embolism.
A: CE-MRA shows a filling defect in the interlobar artery (white arrow) consistent with the expected appearance of a pulmonary embolus (arrow); B: CE-MRA showing an eccentrically located pulmonary embolus that spans the truncus anterior and interlobar artery (arrow); C: Post gadolinium fat saturated breath hold axial spoiled gradient echo image showing bilateral filling defects in the lower lobe pulmonary arteries (interlobar PE-dashed arrow, left lower lobe pulmonary artery-arrow). CE-MRA: Contrast enhanced magnetic resonance angiograph; PE: Pulmonary embolism.
- Citation: Tsuchiya N, Beek EJV, Ohno Y, Hatabu H, Kauczor HU, Swift A, Vogel-Claussen J, Biederer J, Wild J, Wielpütz MO, Schiebler ML. Magnetic resonance angiography for the primary diagnosis of pulmonary embolism: A review from the international workshop for pulmonary functional imaging. World J Radiol 2018; 10(6): 52-64
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1949-8470/full/v10/i6/52.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4329/wjr.v10.i6.52