Copyright
©The Author(s) 2017.
World J Cardiol. Aug 26, 2017; 9(8): 673-684
Published online Aug 26, 2017. doi: 10.4330/wjc.v9.i8.673
Published online Aug 26, 2017. doi: 10.4330/wjc.v9.i8.673
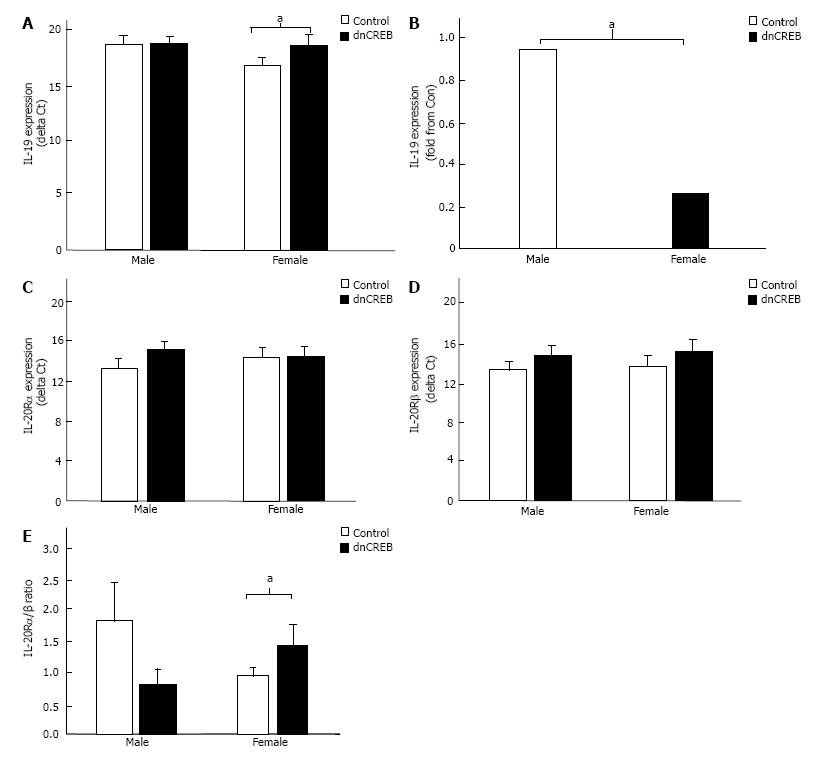
Figure 1 Expression of interleukin-19 and interleukin-20R in the dominant negative cyclic AMP response-element binding protein model of female-dominant heart failure.
A: Female male significantly downregulated IL-19 expression in the setting of dnCREB-mediated heart failure compared to male mice which maintained IL-19 expression; B: A significant difference between sexes; C: IL-20Rα and IL-20Rβ (D) expression were unchanged in either sex; D: However, the ratio between IL-20Rα/β was significantly upregulated in female dnCREB mice. Expression of IL-19 and IL-20R was assessed by qRT-PCR, and ΔCt calculated relative to 18S. The ratio of IL-20Rα/β was calculated as a fold change of α-β within each sex. Data are expressed as mean ± SEM. aP < 0.05, n = 5-9 mice per group. dnCREB: Do-minant negative cyclic AMP response-element binding protein.
- Citation: Bruns DR, Ghincea AR, Ghincea CV, Azuma YT, Watson PA, Autieri MV, Walker LA. Interleukin-19 is cardioprotective in dominant negative cyclic adenosine monophosphate response-element binding protein-mediated heart failure in a sex-specific manner. World J Cardiol 2017; 9(8): 673-684
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1949-8462/full/v9/i8/673.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4330/wjc.v9.i8.673