Copyright
©The Author(s) 2017.
World J Cardiol. Jul 26, 2017; 9(7): 600-608
Published online Jul 26, 2017. doi: 10.4330/wjc.v9.i7.600
Published online Jul 26, 2017. doi: 10.4330/wjc.v9.i7.600
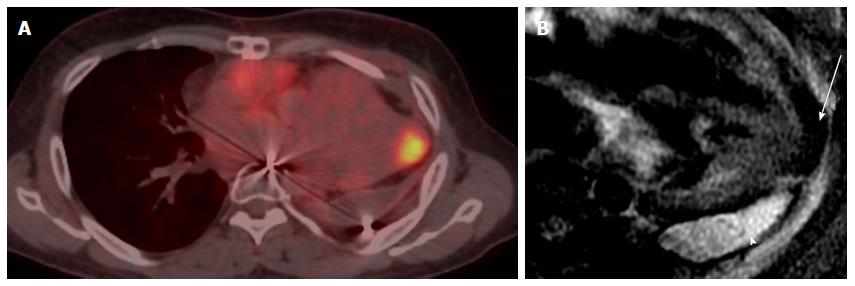
Figure 2 Localization and characterization of abnormal fluorodeoxygluocse activity in the heart.
A: Axial PET-CT images in patient with history of invasive thymoma underwent surgical resection shows intense FDG focal uptake in the cardiac apex highly suspicious for cardiac metastases, review CT component of PET-CT shows area of and soft tissue; B: Four-chamber DE image with triple inversion recovery shows complete fat suppression of the apical activity in keeping with brown fat (arrow), with high signal fluid intensity consistent with post-operative lobulated fluid collection (arrowhead). PET: Positron emission tomography; CT: Computed tomography; FDG: Fluorodeoxygluocse.
- Citation: Fathala A, Abouzied M, AlSugair AA. Cardiac and pericardial tumors: A potential application of positron emission tomography-magnetic resonance imaging. World J Cardiol 2017; 9(7): 600-608
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1949-8462/full/v9/i7/600.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4330/wjc.v9.i7.600