Copyright
©The Author(s) 2016.
World J Cardiol. Sep 26, 2016; 8(9): 553-558
Published online Sep 26, 2016. doi: 10.4330/wjc.v8.i9.553
Published online Sep 26, 2016. doi: 10.4330/wjc.v8.i9.553
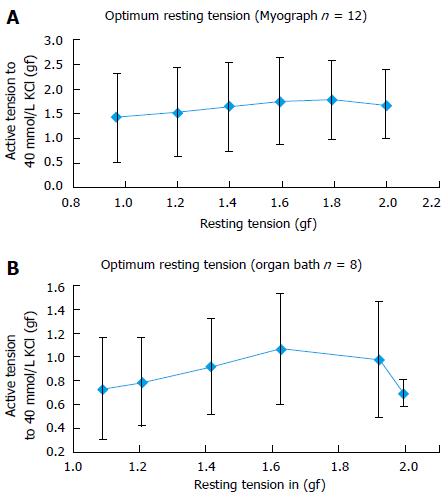
Figure 3 Measurement of Optimal Resting Tension using Multi-wire Myograph (A) and Organ Bath system (B).
A: Total 12 PA rings from four patients were used to perform the experiment. Increasing the resting tension from 1.0 gf to 1.6 gf significantly augmented the 40 mmol/L KCl induced active tension. Increasing the active tension from 1.6 to 2.0 gf initially plateaued off than decreased the 40 mmol/L KCl induced response; B: Total 8 PA rings from four patients were used to perform the experiment. Increasing the resting tension from 1.0 to 1.6 gf significantly augmented the 40 mmol/L KCl induced active tension. Increasing the active tension from 1.6 to 2.0 gf either decreased the 40 mmol/L KCl induced response.
- Citation: Hussain A, Bennett RT, Chaudhry MA, Qadri SS, Cowen M, Morice AH, Loubani M. Characterization of optimal resting tension in human pulmonary arteries. World J Cardiol 2016; 8(9): 553-558
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1949-8462/full/v8/i9/553.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4330/wjc.v8.i9.553