Copyright
©The Author(s) 2016.
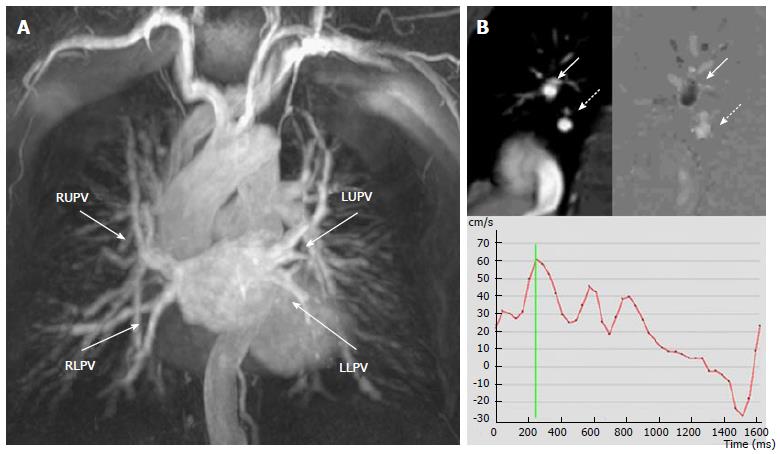
Figure 3 Magnetic resonance scan of a patient with a radiofrequency ablation procedure one month before, mild hemoptysis and fever.
A: Angiography shows normal caliber of the four PVs; B: Phase contrast imaging of the right lower PV. Top left: right pulmonary artery (arrow) and right lower PV (dashed arrow). Top right: Flow map. Black or white signal depends on the direction of the flow. The PV “white flow” (dashed arrow) compares with the opposite direction of flow in the pulmonary artery seen in the same image that is “black” (arrow). Bottom: the resulting velocity-time curve demonstrates normal flow morphology and velocities in the PV. Significant PVS was excluded. RUPV: Right upper pulmonary vein; RLPV: Right lower pulmonary vein; LUPV: Left upper pulmonary vein; LLPV: Left lower pulmonary vein; PV: Pulmonary vein.
- Citation: Pazos-López P, García-Rodríguez C, Guitián-González A, Paredes-Galán E, Álvarez-Moure M&DLG, Rodríguez-Álvarez M, Baz-Alonso JA, Teijeira-Fernández E, Calvo-Iglesias FE, Íñiguez-Romo A. Pulmonary vein stenosis: Etiology, diagnosis and management. World J Cardiol 2016; 8(1): 81-88
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1949-8462/full/v8/i1/81.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4330/wjc.v8.i1.81