Copyright
©The Author(s) 2016.
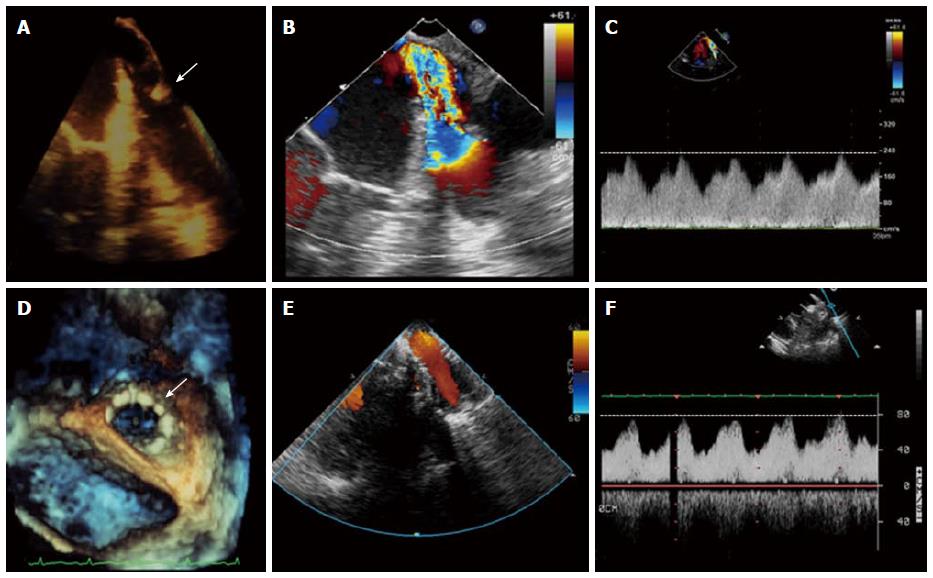
Figure 1 Transesophageal echocardiography of a patient with a recent left lung transplantation and severe congestion in the graft.
A: Narrowing in the common trunk of the left PVs at the level of the sutures (arrow). Color Doppler and Continuous Wave Doppler demonstrate turbulent flow (B) and high velocity (C: peak velocity 2.4 m/s; peak gradient 23 mmHg) across the vessel which is consistent with a significant stenosis. A stent was successfully implanted at the level of the stenosis (D: “en face” 3D echo image view; arrow). Laminar flow (E) and normal velocities (F: peak velocity 0.8 m/s; Peak gradient 2.5 mmHg) were seen after the procedure.
- Citation: Pazos-López P, García-Rodríguez C, Guitián-González A, Paredes-Galán E, Álvarez-Moure M&DLG, Rodríguez-Álvarez M, Baz-Alonso JA, Teijeira-Fernández E, Calvo-Iglesias FE, Íñiguez-Romo A. Pulmonary vein stenosis: Etiology, diagnosis and management. World J Cardiol 2016; 8(1): 81-88
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1949-8462/full/v8/i1/81.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4330/wjc.v8.i1.81