Copyright
©The Author(s) 2015.
World J Cardiol. Sep 26, 2015; 7(9): 511-524
Published online Sep 26, 2015. doi: 10.4330/wjc.v7.i9.511
Published online Sep 26, 2015. doi: 10.4330/wjc.v7.i9.511
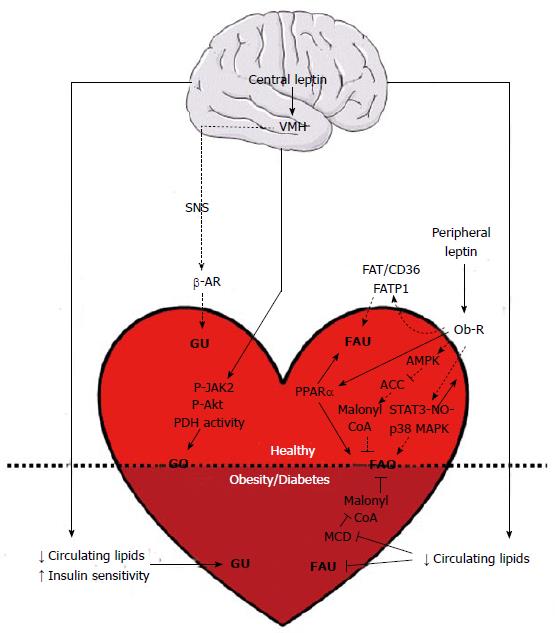
Figure 3 Cardiometabolic effects of leptin in health and obesity.
Triangular and flat arrowheads represent stimulatory and inhibitory effects on the designed targets, respectively. Dotted lines indicate acute leptin effects (appearing between less than an hour and several hours of treatment), while plain lines represent chronic leptin effects (reported after several days or weeks of treatment). ACC: Acetyl-CoA carboxylase; AMPK: AMP-activated protein kinase; β-AR: Beta-adrenergic receptor; FAO: Fatty acid oxidation; FAT/CD36: Fatty acid translocase/cluster of differentiation 36; FATP1: Fatty acid transport protein 1; FAU: Fatty acid uptake; GO: Glucose oxidation; GU: Glucose uptake; MAPK: Mitogen-activated protein kinase; MCD: Malonyl-CoA decarboxylase; NO: Nitric oxide; Ob-R: Leptin receptor; P-Akt: Phosphorylated Akt kinase; PDH: Pyruvate dehydrogenase; P-JAK2: Phosphorylated Janus kinase 2; PPARα: Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha; SNS: Sympathetic nervous system; STAT3: Signal transducer and activator of transcription 3; VMH: Ventromedial hypothalamus. Horizontal black line demarcates differences between the healthy heart and the heart in obesity/diabetes.
- Citation: Hall ME, Harmancey R, Stec DE. Lean heart: Role of leptin in cardiac hypertrophy and metabolism. World J Cardiol 2015; 7(9): 511-524
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1949-8462/full/v7/i9/511.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4330/wjc.v7.i9.511