Copyright
©The Author(s) 2015.
World J Cardiol. Dec 26, 2015; 7(12): 882-888
Published online Dec 26, 2015. doi: 10.4330/wjc.v7.i12.882
Published online Dec 26, 2015. doi: 10.4330/wjc.v7.i12.882
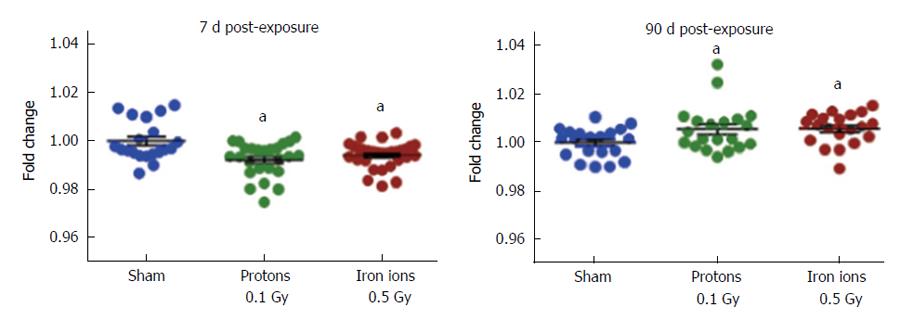
Figure 1 Methylation of genomic DNA isolated from hearts of male C57Bl/6 mice at 7 d and 90 d after exposure to protons (150 MeV, 0.
1 Gy) or iron ions (600 MeV/n, 0.5 Gy). DNA methylation of the open reading frame 1 of long interspersed nuclear element-1, a transposable element that comprises about 20% of the mouse genome, as assessed by pyrosequencing and indicated as fold change compared to sham-irradiated controls. Each group contained 4-5 animals. Horizontal lines indicate average ± standard error of the mean. aP < 0.05 vs the sham-irradiated control group.
- Citation: Boerma M, Nelson GA, Sridharan V, Mao XW, Koturbash I, Hauer-Jensen M. Space radiation and cardiovascular disease risk. World J Cardiol 2015; 7(12): 882-888
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1949-8462/full/v7/i12/882.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4330/wjc.v7.i12.882