Copyright
©The Author(s) 2015.
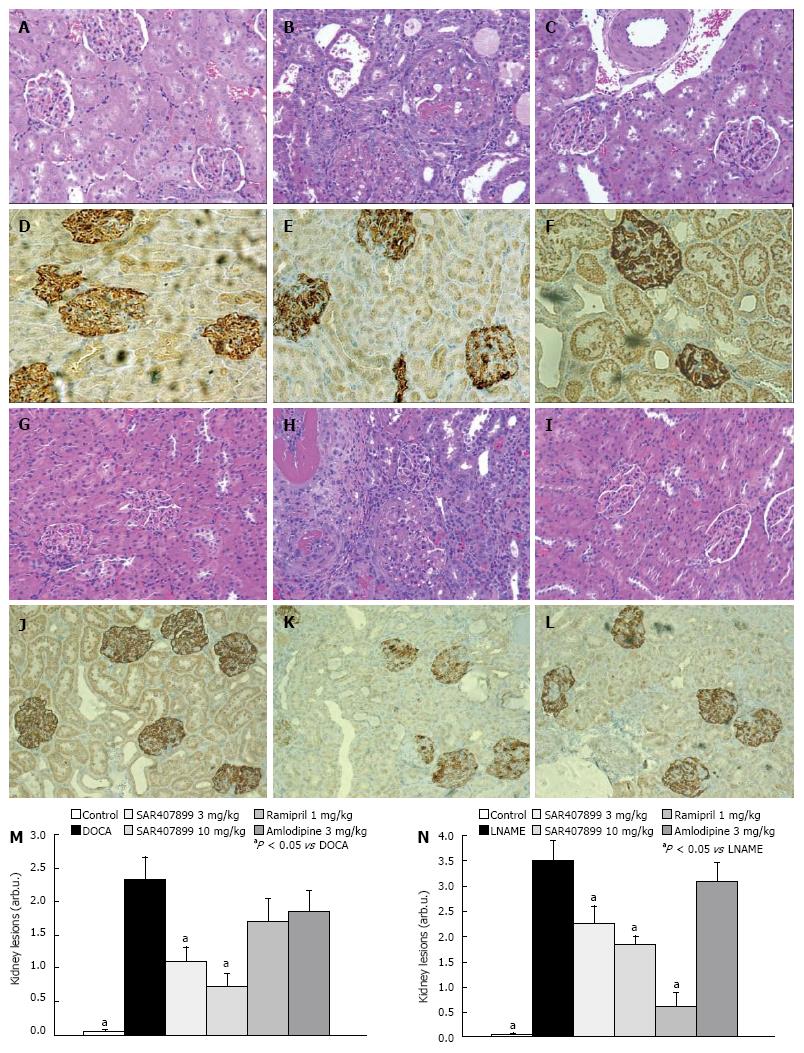
Figure 5 Histological examination of the effect of SAR407899 on the kidney.
A-C: Haematoxylin eosin staining of normal glomeruli in control rats (left), sclerotic changes, dilation and hypertrophy of glomeruli of deoxycorticosterone acetate (DOCA) rats (center) and protective effects of SAR407899 at 10 mg/kg (right); D-F: Podocin staining in kidneys. Upon DOCA treatment, massive loss of podocytes can be detected. SAR407899 at 10 mg/kg exerts a protective effect in the kidneys of DOCA rats and rescues podocytes; G-I: Haematoxylin eosin staining of normal glomeruli in control rats (left), severe fibrotic changes, infiltration of leukocytes, and hypertrophy of glomeruli of Nω-Nitro-L-arginine methyl ester hydrochloride (LNAME) rats (center), protective effects of SAR407899 at 10 mg/kg (right); J-L: Loss of podocytes upon LNAME treatment. SAR407899 at 10 mg/kg protected against loss of podocytes. Summary of kidney lesions and effect of SAR407899 and reference substances in DOCA (M) and LNAME rats (N). A, D, G, J: Control; B, E: DOCA; H, K: LNAME; C, F, I, L: SAR407899 10 mg/kg.
- Citation: Löhn M, Plettenburg O, Kannt A, Kohlmann M, Hofmeister A, Kadereit D, Monecke P, Schiffer A, Schulte A, Ruetten H, Ivashchenko Y. End-organ protection in hypertension by the novel and selective Rho-kinase inhibitor, SAR407899. World J Cardiol 2015; 7(1): 31-42
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1949-8462/full/v7/i1/31.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4330/wjc.v7.i1.31