Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Cardiol. Jun 26, 2014; 6(6): 353-366
Published online Jun 26, 2014. doi: 10.4330/wjc.v6.i6.353
Published online Jun 26, 2014. doi: 10.4330/wjc.v6.i6.353
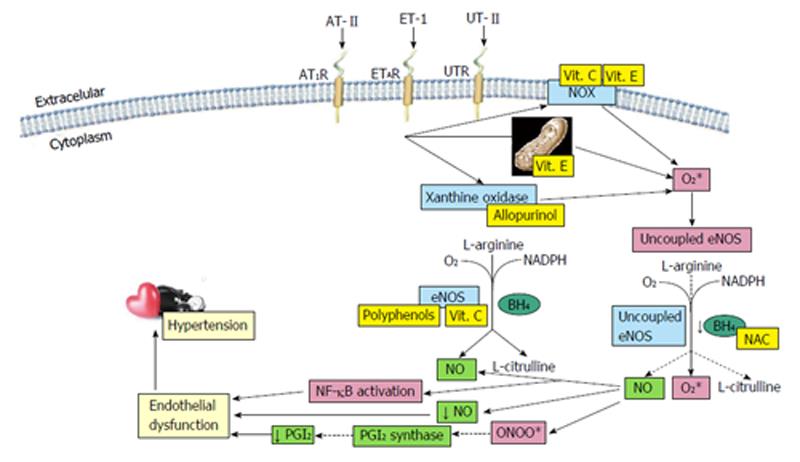
Figure 1 Schematic summary of the role of vascular oxidative stress in the pathogenesis of hypertension and the mechanisms of exogenous antioxidant accounting for anti-hypertensive effects.
AT-II: Angiotensin II; AT1R: Type 1 angiotensin II receptor; ET-1: Endothelin 1; ETAR: Type A endothelin receptor; UT-II: Urotensin II; UTR: Urotensin-II receptor; NO: Nitric oxide; eNOS: Endothelial nitric oxide synthase; PGI2: Prostacyclin; NAC: N-Acetylcysteine; NOX: NADPH oxidase; NF-κB: Nuclear factor kappa B.
- Citation: González J, Valls N, Brito R, Rodrigo R. Essential hypertension and oxidative stress: New insights. World J Cardiol 2014; 6(6): 353-366
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1949-8462/full/v6/i6/353.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4330/wjc.v6.i6.353