Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Cardiol. May 26, 2014; 6(5): 314-326
Published online May 26, 2014. doi: 10.4330/wjc.v6.i5.314
Published online May 26, 2014. doi: 10.4330/wjc.v6.i5.314
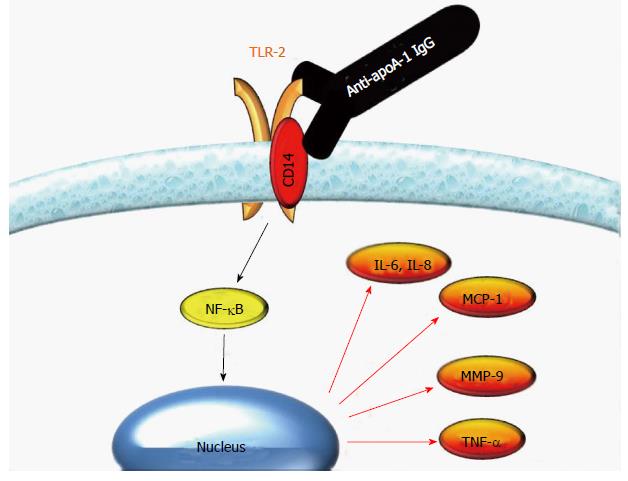
Figure 3 Autoantibodies against apolipoprotein A-1 IgG elicit a pro-inflammatory response through Toll-like receptor 2/CD14 complex on human macrophages.
Autoantibodies against apolipoprotein A-1 (anti-apoA-1) IgG specifically bind to Toll-like receptor (TLR)2 due to conformational homology between apoA-1 and TLR2. In the presence of CD14, the binding of anti-apoA-1 IgG to TLR2 induces a nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells (NF-κB)-dependent production of pro-inflammatory cytokines. MMP-9: Matrix-metalloproteinases; IL-8: Interleukin-8.
- Citation: Vuilleumier N, Montecucco F, Hartley O. Autoantibodies to apolipoprotein A-1 as a biomarker of cardiovascular autoimmunity. World J Cardiol 2014; 6(5): 314-326
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1949-8462/full/v6/i5/314.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4330/wjc.v6.i5.314