Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Cardiol. Apr 26, 2014; 6(4): 183-195
Published online Apr 26, 2014. doi: 10.4330/wjc.v6.i4.183
Published online Apr 26, 2014. doi: 10.4330/wjc.v6.i4.183
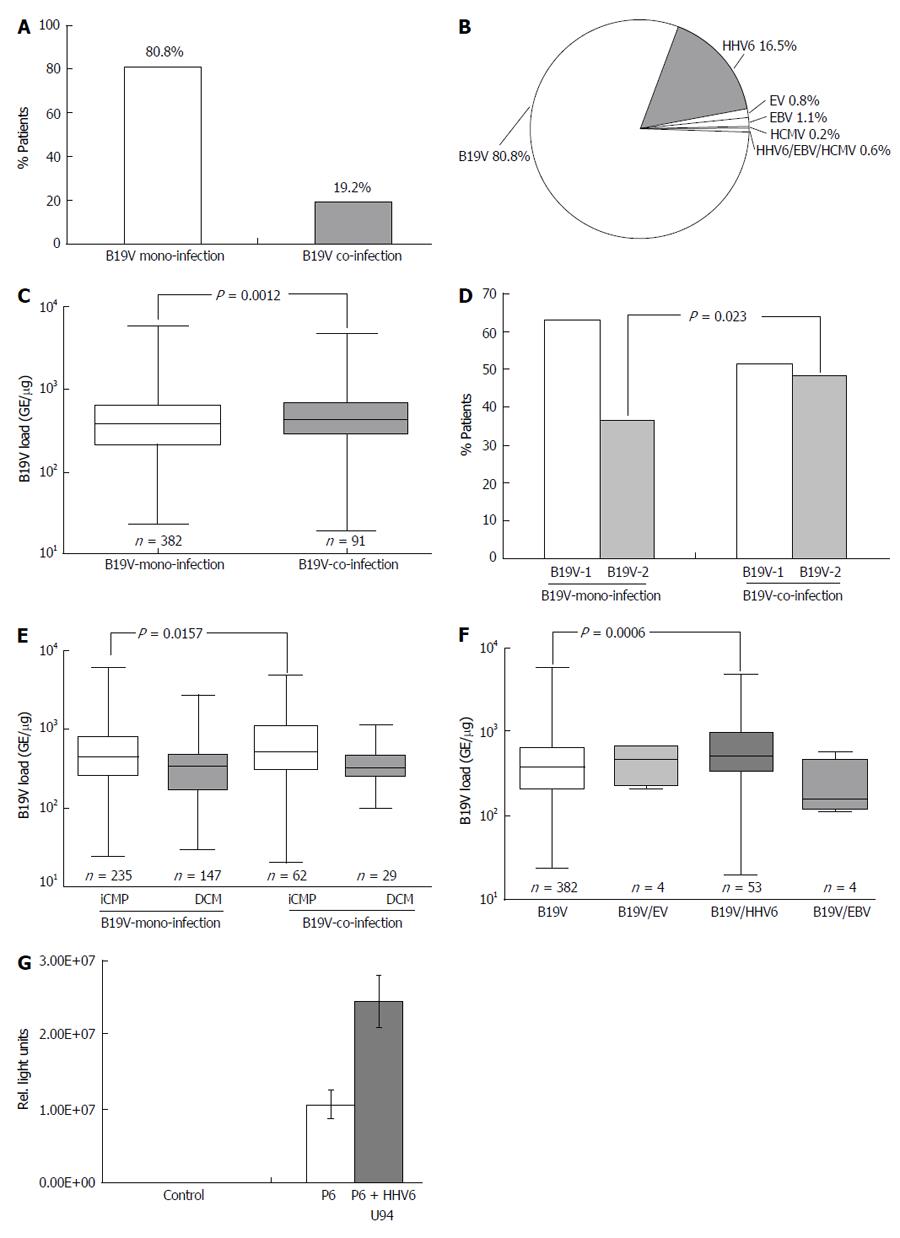
Figure 6 Distribution of B19V-coinfection with cardiotropic viruses.
A: In endomyocardial biopsies determined by virus-specific nPCR; B: Frequency of B19V-coinfection with cardiotropic viruses; C: qPCR of B19V loads in B19V mono- and co-infection; D: Distribution of B19V-genotype 1 and 2 in B19V mono- and co-infection in endomyocardial biopsies (EMBs); E: B19V loads of B19V mono- and co-infection in EMBs of patients with iCMP and DCM. One-way Anova was highly significant (P < 0.0001); F: B19V loads of B19V mono- and co-infection with cardiotropic viruses. One-way Anova was highly significant (P = 0.0091); G: Luciferase reporter assay to determine transactivation capacity of the HHV6-U94 transactivator on the B19V P6-promoter activity. P < 0.05 is statistically significant (two-tailed T-test). HHV6: Human herpesvirus 6; EV: Enterovirus; HCMV: Human cytomegalovirus; EBV: Epstein-Barr virus; DCM: Dilated cardiomyopathy; iCMP: Inflammatory cardiomyopathy; qPCR: Quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction.
- Citation: Bock CT, Düchting A, Utta F, Brunner E, Sy BT, Klingel K, Lang F, Gawaz M, Felix SB, Kandolf R. Molecular phenotypes of human parvovirus B19 in patients with myocarditis. World J Cardiol 2014; 6(4): 183-195
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1949-8462/full/v6/i4/183.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4330/wjc.v6.i4.183