Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Cardiol. Apr 26, 2014; 6(4): 175-182
Published online Apr 26, 2014. doi: 10.4330/wjc.v6.i4.175
Published online Apr 26, 2014. doi: 10.4330/wjc.v6.i4.175
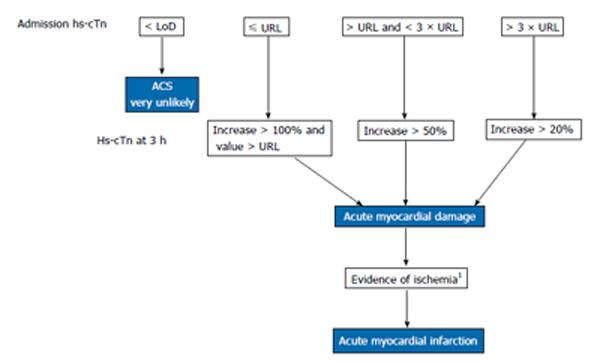
Figure 1 Algorithm for the rapid evaluation of clinically suspected acute myocardial infarction with high-sensitivity cardiac troponin testing.
This algorithm is based on best current knowledge and may have to be modified with upcoming new data. This approach at least guarantees that the changes will be above the analytical and biological variation. It is important to note that hs-cTn changes over a 3 h period in patients presenting late after AMI onset may be less than 20%. For hs-cTnT some studies favour absolute changes over relative concentration changes. 1Evidence of acute myocardial ischemia by new ECG changes and/or new imaging corroborations. Hs-cTn: High-sensitivity cardiac troponin; URL: 99th percentile upper reference limit of healthy controls; ACS: Acute coronary syndrome; LoD: Lower limit of detection; AMI: Acute myocardial infarction; ECG: Electrocardiogram.
- Citation: Mair J. High-sensitivity cardiac troponins in everyday clinical practice. World J Cardiol 2014; 6(4): 175-182
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1949-8462/full/v6/i4/175.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4330/wjc.v6.i4.175