Copyright
©2013 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Cardiol. Nov 26, 2013; 5(11): 404-409
Published online Nov 26, 2013. doi: 10.4330/wjc.v5.i11.404
Published online Nov 26, 2013. doi: 10.4330/wjc.v5.i11.404
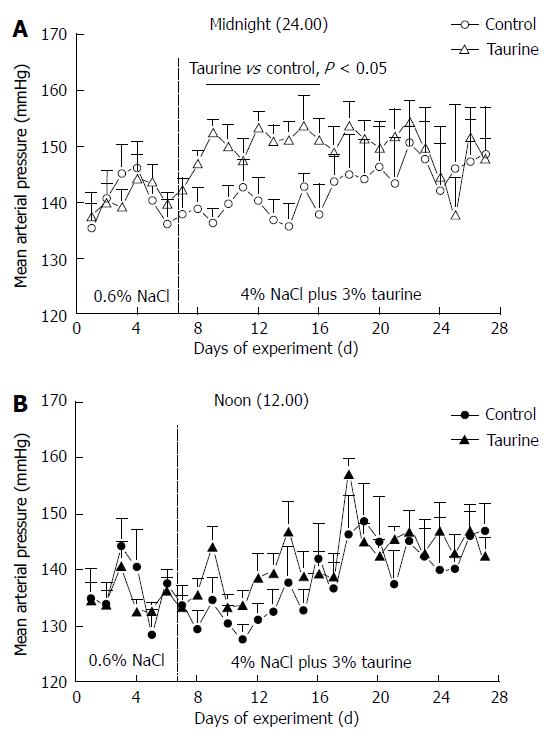
Figure 2 Group averages of mean arterial pressure in control (n = 7) and taurine (n = 12) treated groups at midnight (A) and at noon (B).
The daytime mean arterial pressures were not significantly different between groups throughout the study. The vertical dashed line at day 7 indicates the day that the high NaCl diet and taurine supplementation began. Statistical comparisons were performed by one-way analysis of variance and post hoc Duncan’s multiple range test.
- Citation: Suwanich A, Wyss JM, Roysommuti S. Taurine supplementation in spontaneously hypertensive rats: Advantages and limitations for human applications. World J Cardiol 2013; 5(11): 404-409
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1949-8462/full/v5/i11/404.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4330/wjc.v5.i11.404