Copyright
©2012 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Cardiol. Apr 26, 2012; 4(4): 90-102
Published online Apr 26, 2012. doi: 10.4330/wjc.v4.i4.90
Published online Apr 26, 2012. doi: 10.4330/wjc.v4.i4.90
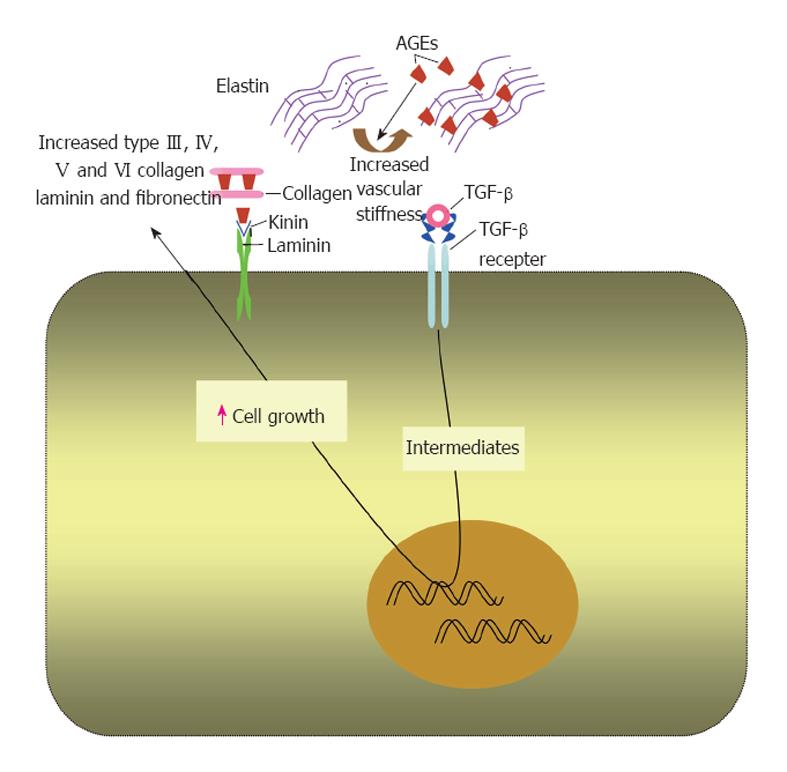
Figure 2 Effects of advanced glycation end products on extracellular matrix proteins.
In extracellular matrix, advanced glycation end products (AGEs) form on different molecules as collagen, laminin and elastin. This alters the physiological properties of the matrix and increases its stiffness. AGEs upregulate transforming growth factor (TGF)-β that increases the production of extracellular matrix components by binding to its receptor.
- Citation: Hegab Z, Gibbons S, Neyses L, Mamas MA. Role of advanced glycation end products in cardiovascular disease. World J Cardiol 2012; 4(4): 90-102
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1949-8462/full/v4/i4/90.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4330/wjc.v4.i4.90