Copyright
©2011 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Cardiol. Sep 26, 2011; 3(9): 281-302
Published online Sep 26, 2011. doi: 10.4330/wjc.v3.i9.281
Published online Sep 26, 2011. doi: 10.4330/wjc.v3.i9.281
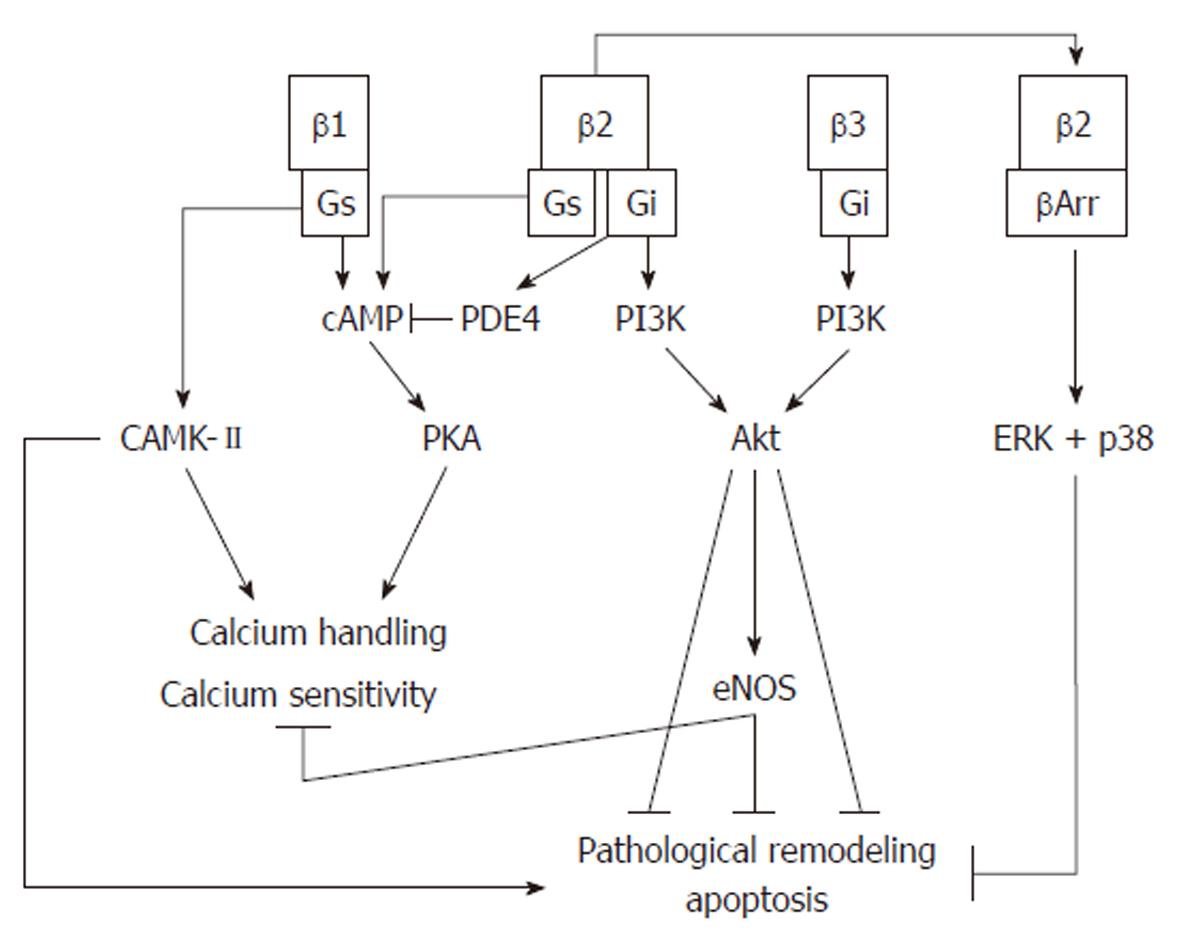
Figure 2 β-adrenergic signaling pathways.
β1-adrenergic receptors activate protein kinase A (PKA), which regulates calcium sensitivity and calcium handling. Prolonged activation of this receptor activates a harmful calmodulin-dependent protein kinase (CAMK)-II pathway which is pro-apoptotic and induces pathological remodeling. β2-adrenergic receptors also activate PKA, but prolonged activation causes a switch to Gi signaling which activates PDE4, inhibiting cAMP formation, and activates the cardioprotective phosphoinositol-3 kinase (PI3K)/protein kinase B (Akt) pathway. Desensitization of β2-adrenergic receptors by β-arrestin can recruit p38 and extracellular-signal-regulated kinase (ERK), which protect the cell from apoptosis. β3-adrenergic receptors produce a negative inotropic effect which is mediated by nitric oxide produced via the PI3K/Akt pathway.
- Citation: Sharma V, McNeill JH. Parallel effects of β-adrenoceptor blockade on cardiac function and fatty acid oxidation in the diabetic heart: Confronting the maze. World J Cardiol 2011; 3(9): 281-302
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1949-8462/full/v3/i9/281.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4330/wjc.v3.i9.281