Copyright
©2011 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Cardiol. Jul 26, 2011; 3(7): 230-247
Published online Jul 26, 2011. doi: 10.4330/wjc.v3.i7.230
Published online Jul 26, 2011. doi: 10.4330/wjc.v3.i7.230
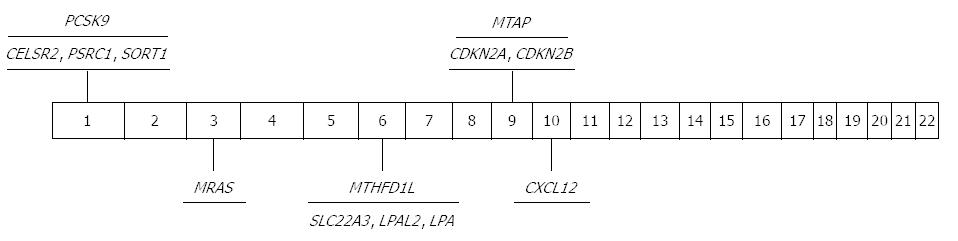
Figure 1 Significant genome-wide association study findings in coronary heart disease.
CELSR2: Cadherin EGF LAG seven-pass G-type receptor 2; PSRC1: Proline/serine-rich coiled-coil 1; SORT1: Sortilin 1; PCSK9: Proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9; MRAS: Ras-related protein M-Ras; MTHFD1L: Methylenetetrahydrofolate dehydrogenase (NADP+ dependent) 1-like; SLC22A3: Solute carrier family 22 (extraneuronal monoamine transporter), member 3; LPAL2: Lipoprotein, Lp(a)-like 2 pseudogene; LPA: Lipoprotein Lp(a); CDKN2A: Cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor 2A; CDKN2B: Cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor 2B; MTAP: Methylthioadenosine phosphorylase; CXCL12: Chemokine (C-X-C motif) ligand 12.
- Citation: Jeemon P, Pettigrew K, Sainsbury C, Prabhakaran D, Padmanabhan S. Implications of discoveries from genome-wide association studies in current cardiovascular practice. World J Cardiol 2011; 3(7): 230-247
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1949-8462/full/v3/i7/230.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4330/wjc.v3.i7.230