Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Cardiol. Apr 26, 2025; 17(4): 105021
Published online Apr 26, 2025. doi: 10.4330/wjc.v17.i4.105021
Published online Apr 26, 2025. doi: 10.4330/wjc.v17.i4.105021
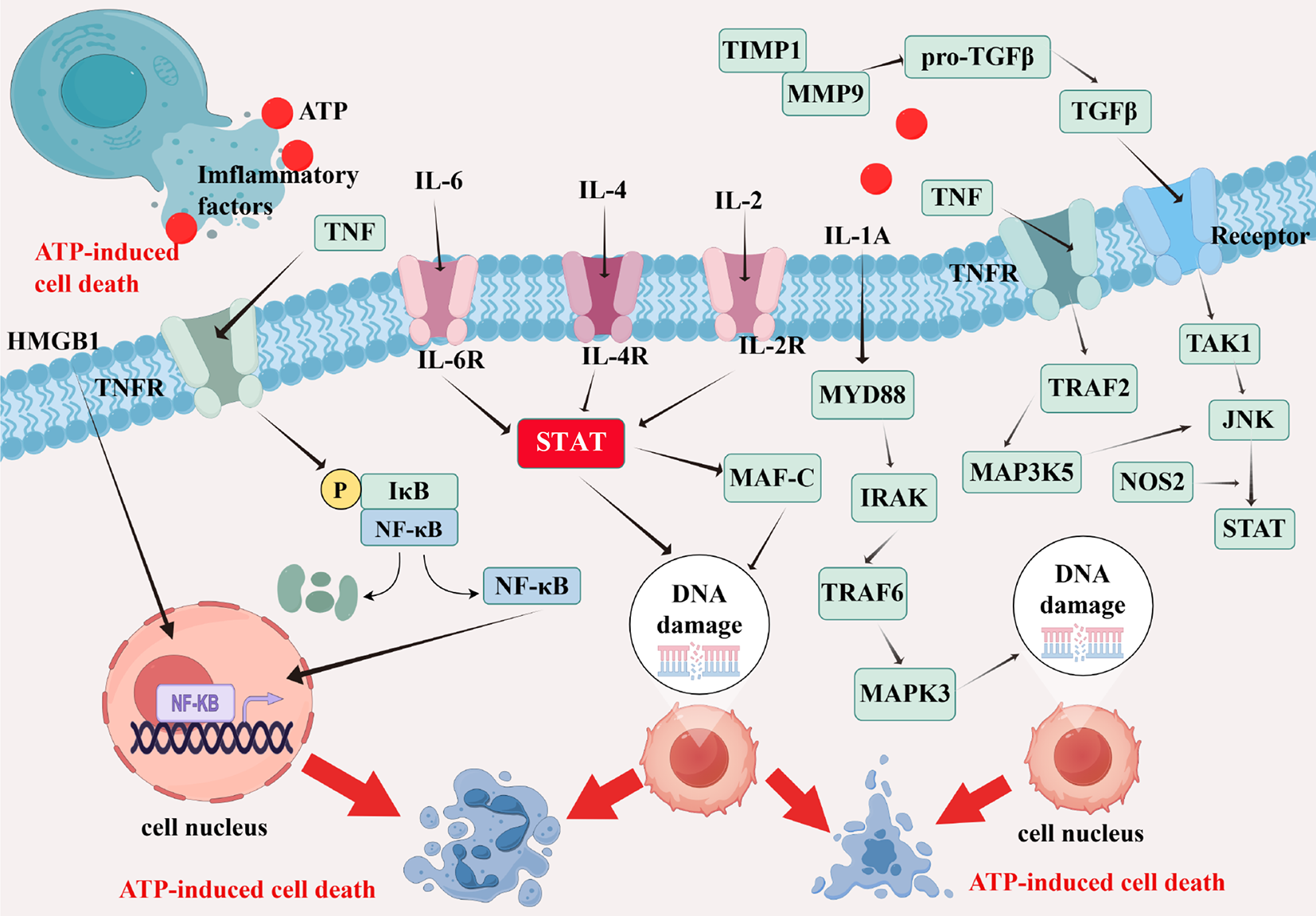
Figure 3 Adenosine triphosphate triggers the release of immune-inflammatory factors from cells, activating immune pathways.
ATP: Adenosine triphosphate; HMGB1: High mobility group box-1 protein; TNF: Tumor necrosis factor ; TNFR: Tumor necrosis factor receptor; NF-κB: Nuclear factor-kappa B; IκB: I kappa B; DNA: Deoxyribonucleic acid; IL-6: Interleukin-6; IL-6R: Interleukin-6 receptor; IL-4: Interleukin-4; IL-4R: Interleukin-4 receptor; IL-2: Interleukin-2; IL-2R: Interleukin-2 receptor; IL-1A: Interleukin-1a; STAT: Signal transducer and activator of transcription; MAF-C: Musculoaponeurotic fibrosarcoma oncogene; MYD88: The canonical adaptor for inflammatory signaling pathways downstream of members of the Toll-like receptor (TLR) and interleukin-1 (IL-1) receptor families; IRAK: IL-1R-associated kinase; TRAF6: TNF receptor associated factor 6; MAPK3: Mitogen-activated protein kinase 3; TRAF2: TNF receptor associated factor 2; MAP3K5: Mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase kinase 5; TIMP1: The tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases 1; MMP9: Matrix metallopeptidase 9; pro-TGFβ: Pro-transforming growth factor-beta; TAK1: Transforming growth factor beta-activated kinase 1; JNK: C-Jun N-terminal kinase; NOS2: Nitric oxide synthase. Drawn by Figdraw.
- Citation: Zhang JJ, Cheng L, Qiao Q, Xiao XL, Lin SJ, He YF, Sha RL, Sha J, Ma Y, Zhang HL, Ye XR. Adenosine triphosphate-induced cell death in heart failure: Is there a link? World J Cardiol 2025; 17(4): 105021
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1949-8462/full/v17/i4/105021.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4330/wjc.v17.i4.105021